In today’s environmentally conscious and economically prudent world, understanding the electricity consumption of our household appliances is more critical than ever. Among these essential devices, the fridge freezer stands as a constant energy consumer, diligently preserving our food day in and day out. While its role in our daily lives is indispensable, its continuous operation can contribute significantly to our household energy bills and overall carbon footprint. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the intricacies of fridge freezer electricity consumption, exploring the myriad factors that influence its energy usage, providing actionable strategies to minimize its environmental impact and operational costs, and offering insights into the future of energy-efficient refrigeration technology. Prepare to gain a profound understanding of how your fridge freezer consumes energy and how you can make informed choices to optimize its efficiency.
Deconstructing the Energy Drain: Factors Influencing Fridge Freezer Electricity Consumption
The amount of electricity your fridge freezer consumes is not a fixed entity; rather, it is a dynamic value influenced by a confluence of factors. Understanding these elements is the first crucial step towards effective energy management.

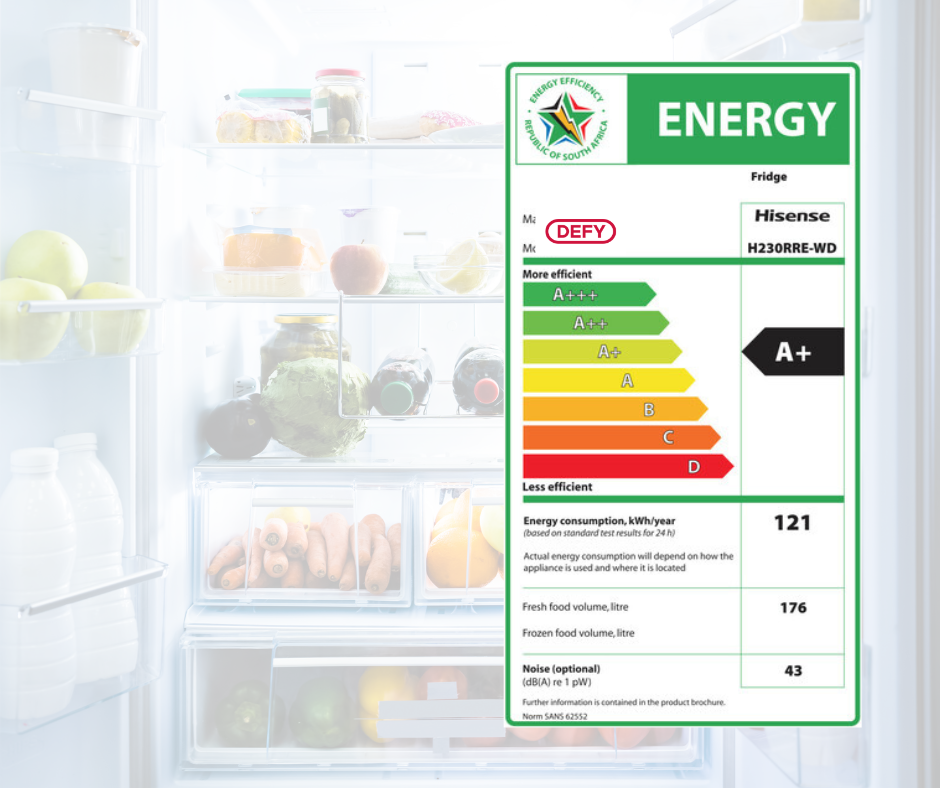
- Age and Model Efficiency: Older fridge freezer models are often significantly less energy-efficient than their modern counterparts. Technological advancements have led to substantial improvements in insulation, compressor design, and cooling mechanisms, resulting in lower energy consumption in newer appliances. Energy efficiency ratings, such as the European Union’s energy labels (ranging from A to G), provide a clear indication of a model’s energy performance. Choosing a higher-rated model can lead to considerable long-term savings.
- Size and Capacity: Logically, larger fridge freezers with greater internal volumes require more energy to maintain their temperature. While a larger capacity might be necessary for larger households, opting for a size that accurately matches your needs can prevent unnecessary energy expenditure. A partially empty large fridge freezer still consumes energy to cool the unused space.
- Temperature Settings: The thermostat settings for both the refrigerator and freezer compartments directly impact energy consumption. Lower temperatures demand more energy. The generally recommended temperature for a refrigerator is between 3°C and 5°C (37°F and 41°F), while the ideal freezer temperature is around -18°C (0°F). Setting these temperatures lower than necessary will lead to increased electricity consumption without providing any significant benefit to food preservation.
- Door Usage and Seal Integrity: Every time the fridge freezer door is opened, cold air escapes, and the appliance has to work harder to restore the internal temperature. Frequent and prolonged door openings significantly increase energy usage. Furthermore, worn or damaged door seals allow cold air to leak out continuously, forcing the compressor to run more often. Regularly inspecting and maintaining the door seals is crucial for energy efficiency.
- Frost Buildup: In manual defrost fridge freezers, the accumulation of frost on the evaporator coils acts as an insulator, hindering the cooling process and forcing the compressor to work harder and longer, leading to increased electricity consumption. Regularly defrosting your appliance is essential for maintaining its efficiency. Frost-free models mitigate this issue by automatically defrosting periodically.
- Ambient Temperature and Ventilation: The temperature of the room where the fridge freezer is located can also affect its energy consumption. If the ambient temperature is high, the appliance will need to work harder to maintain its internal coolness. Ensuring adequate ventilation around the fridge freezer is also important, as restricted airflow can impede heat dissipation and reduce efficiency. Avoid placing your fridge freezer near heat sources such as ovens, radiators, or direct sunlight.
- Food Placement and Organization: Proper food placement can influence air circulation within the fridge freezer. Overpacking can restrict airflow, leading to uneven cooling and increased energy consumption. Organizing food in a way that allows for efficient air circulation ensures that the appliance operates optimally without overworking.
Empowering Savings: Practical Strategies to Reduce Fridge Freezer Electricity Consumption

Implementing a few mindful habits and maintenance practices can significantly reduce the electricity consumption of your fridge freezer, leading to lower energy bills and a smaller environmental footprint.
- Optimize Temperature Settings: Ensure your refrigerator is set between 3°C and 5°C and your freezer at -18°C. Use a thermometer to verify the accuracy of the internal temperature.
- Minimize Door Openings: Think before you open the door and try to retrieve all the items you need at once. Avoid leaving the door open for extended periods.
- Check and Maintain Door Seals: Regularly inspect the door seals for any signs of damage or wear. Clean them with warm soapy water to ensure a tight seal. If the seals are damaged, replace them promptly.
- Defrost Regularly (for manual defrost models): Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for defrosting your fridge freezer. Don’t allow excessive frost to build up.
- Ensure Proper Ventilation: Leave adequate space around the sides, top, and back of your fridge freezer to allow for proper air circulation. Avoid placing it in enclosed spaces.
- Keep the Condenser Coils Clean: The condenser coils, usually located at the back or underneath the fridge freezer, dissipate heat. Dust and debris buildup on these coils can reduce their efficiency. Clean them periodically with a vacuum cleaner or a soft brush.
- Allow Hot Food to Cool Before Refrigerating: Placing hot food directly into the fridge freezer raises the internal temperature, forcing the appliance to work harder to cool it down. Let food cool to room temperature first.
- Organize Your Food Efficiently: Arrange food items in a way that promotes good air circulation and makes it easy to find what you need quickly, minimizing door opening times.
- Consider Upgrading to a More Energy-Efficient Model: If your fridge freezer is old, consider investing in a newer model with a high energy efficiency rating. The long-term savings on electricity bills can often outweigh the initial cost. Look for models with features like improved insulation, variable-speed compressors, and smart energy management systems.
- Utilize Energy-Saving Modes (if available): Some modern fridge freezers come with energy-saving modes, such as “vacation mode,” which can be activated when you are away for an extended period. These modes optimize the appliance’s operation for minimal energy consumption.

The Future of Cold: Innovations in Energy-Efficient Refrigeration
The quest for ever-greater energy efficiency in fridge freezers is an ongoing process, driven by environmental concerns and consumer demand. Technological advancements continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible, promising even more energy-saving solutions in the future.
- Variable Speed Compressors: Unlike traditional compressors that operate at a constant speed, variable speed compressors can adjust their cooling output based on the actual cooling demand. This results in more consistent temperatures and significant energy savings.
- Improved Insulation Materials: Advancements in insulation technology are leading to the development of thinner yet more effective insulation materials, allowing for larger internal capacities without increasing external dimensions or energy consumption.
- Smart Sensors and Controls: Integration of smart sensors and sophisticated control systems allows fridge freezers to monitor internal and external conditions and adjust their operation accordingly, optimizing energy usage. Features like door open alarms and temperature monitoring can further contribute to energy savings.
- Alternative Refrigerants: The industry is transitioning towards more environmentally friendly refrigerants with lower global warming potential, further reducing the overall environmental impact of fridge freezers.
- Vacuum Insulation Panels (VIPs): VIPs offer significantly higher thermal resistance compared to conventional insulation materials, allowing for thinner walls and increased internal volume while minimizing heat transfer and energy loss.
- Integration with Smart Home Systems: Future fridge freezers are likely to be increasingly integrated with smart home ecosystems, allowing for remote monitoring and control of energy consumption and temperature settings.

Conclusion: Making Informed Choices for a Sustainable Future
Understanding the electricity consumption of your fridge freezer is not just about saving money on your energy bills; it’s about contributing to a more sustainable future. By being mindful of the factors that influence energy usage and implementing practical energy-saving strategies, you can significantly reduce your environmental impact. When it’s time to replace your old appliance, choosing an energy-efficient model with a high rating is a crucial step towards long-term savings and environmental responsibility. The ongoing innovations in refrigeration technology offer a glimpse into a future where our essential appliances operate with maximum efficiency and minimal environmental cost. By staying informed and making conscious choices, we can all play a part in unlocking a more energy-efficient and sustainable way of living. The humble fridge freezer, often taken for granted, plays a vital role in this endeavor, and understanding its energy dynamics empowers us to make smarter, more sustainable decisions.