In the critical landscape of healthcare, the integrity of vaccines stands as a cornerstone of public health. Maintaining the potency and efficacy of these life-saving biological preparations hinges significantly on the precise and reliable conditions under which they are stored. At the heart of this crucial process lies the vaccine storage refrigerator – a specialized piece of equipment engineered to provide the stable and meticulously controlled environment necessary to preserve the delicate nature of vaccines. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the intricacies of vaccine storage refrigerators, exploring their essential features, the stringent regulatory requirements governing their use, the various types available, and the best practices for ensuring optimal performance and, ultimately, the safety and effectiveness of the vaccines they safeguard.
Understanding the Critical Importance of Proper Vaccine Storage
Vaccines are complex biological products that are sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Exposure to temperatures outside the recommended range, even for short periods, can lead to irreversible damage, rendering them ineffective. This not only compromises the individual receiving the vaccine but also undermines public health efforts and can lead to a loss of trust in vaccination programs. Therefore, investing in a high-quality, purpose-built vaccine storage refrigerator is not merely an expense; it is a fundamental necessity for any healthcare provider, pharmacy, or institution involved in vaccine administration. The consequences of improper storage can be severe, including reduced or complete loss of potency, necessitating revaccination and potentially leading to inadequate protection against preventable diseases. Furthermore, administering a compromised vaccine can erode patient confidence and create significant liability issues.
Key Features and Technologies in Vaccine Storage Refrigerators
Vaccine storage refrigerators are distinct from standard domestic or even commercial refrigerators due to their advanced features designed specifically for the sensitive nature of vaccines. These features are crucial for maintaining the required temperature uniformity and stability:
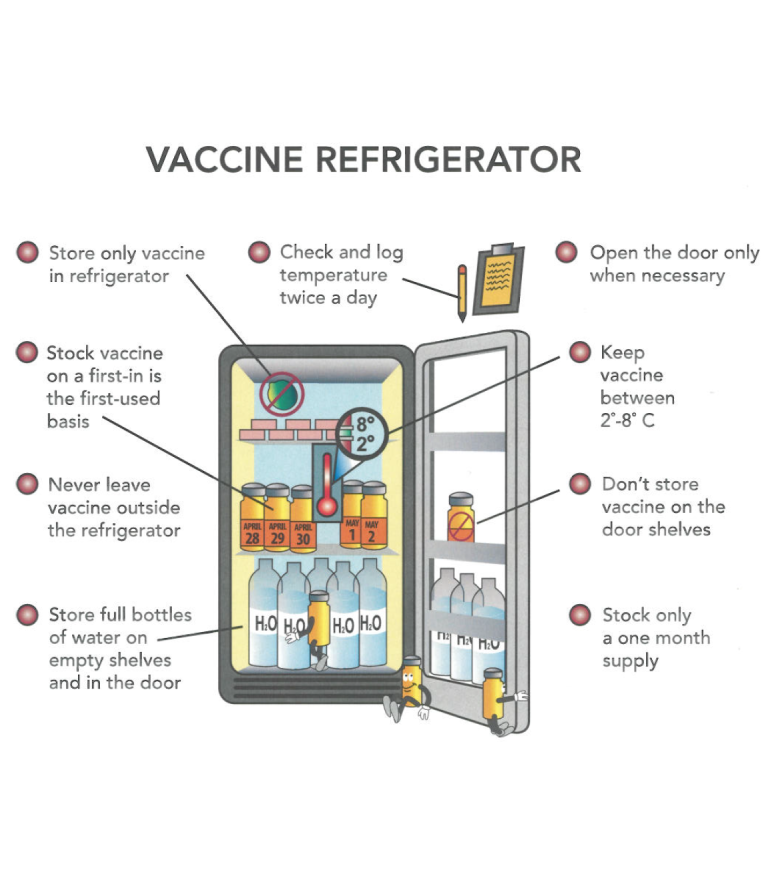
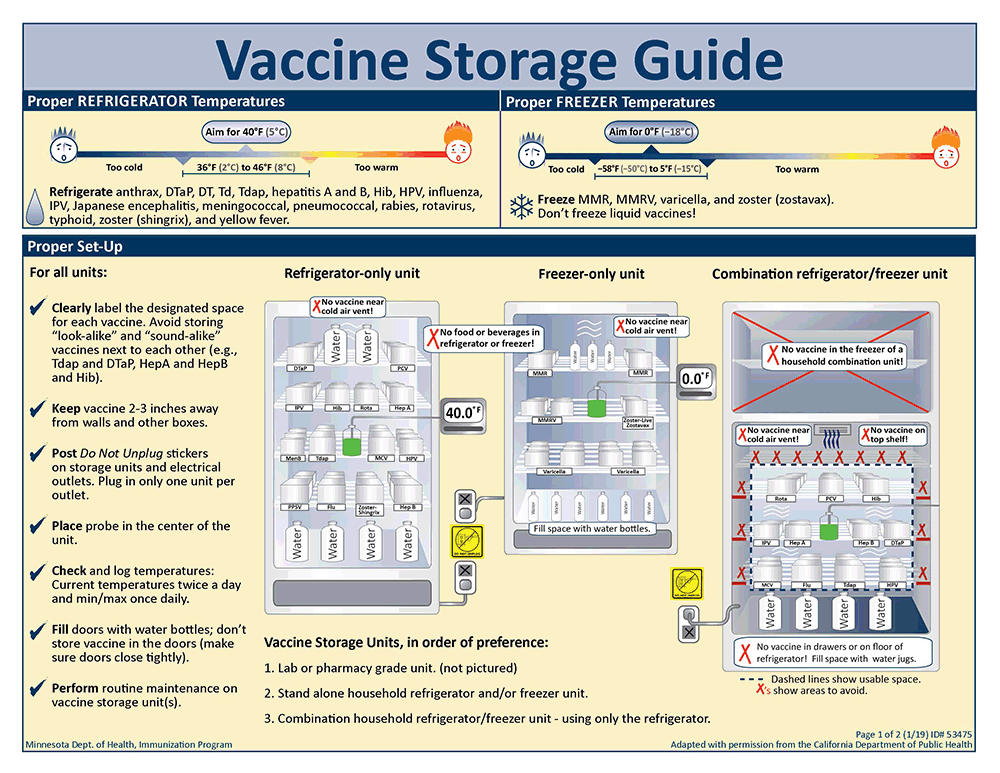
- Precise Temperature Control: Unlike general-purpose refrigerators that can experience significant temperature variations, vaccine refrigerators are equipped with sophisticated temperature control systems that maintain a consistent temperature within the narrow recommended range (typically between 2°C and 8°C, but always verify specific manufacturer guidelines for each vaccine). Digital temperature controllers with alarms are standard, providing continuous monitoring and immediate alerts for any deviations.
- Forced-Air Circulation: Many high-quality vaccine refrigerators utilize forced-air circulation systems. This technology ensures even temperature distribution throughout the entire cabinet, eliminating hot or cold spots that can compromise vaccine integrity. Consistent airflow is paramount for maintaining uniformity, regardless of where the vaccines are placed within the unit.
- Digital Temperature Monitoring and Data Logging: Modern vaccine refrigerators often incorporate advanced digital temperature monitoring systems with data logging capabilities. These systems provide a continuous record of temperature fluctuations, allowing healthcare professionals to track and document storage conditions. This data is invaluable for compliance with regulatory requirements and for identifying any potential temperature excursions. Many systems offer real-time monitoring and remote alerts.
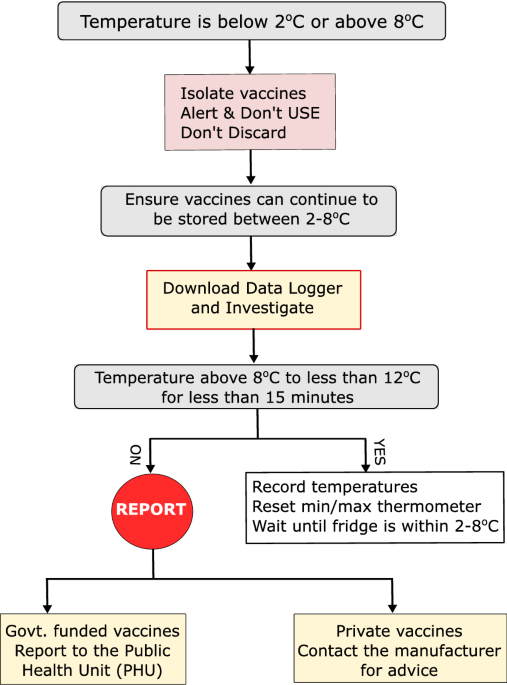
- Alarm Systems: Robust alarm systems are a critical safety feature. These alarms are triggered by temperature deviations outside the acceptable range, power failures, or door ajar situations, providing timely warnings to allow for corrective action and prevent vaccine spoilage. Both audible and visual alarms are common.
- Secure Locking Mechanisms: To prevent unauthorized access and ensure the security of valuable vaccine supplies, vaccine refrigerators are typically equipped with secure locking mechanisms. This is particularly important in busy healthcare settings.
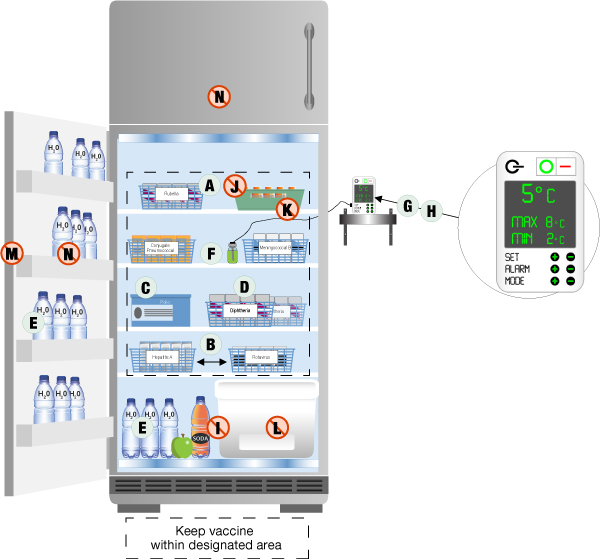
- Optimized Storage Layout: The internal design of vaccine refrigerators often includes adjustable shelves and compartments designed to facilitate organized storage and easy retrieval of vaccines while promoting proper air circulation.
- Self-Closing Doors: To minimize temperature fluctuations caused by open doors, many vaccine refrigerators feature self-closing doors. This seemingly small feature plays a significant role in maintaining a stable internal environment.
Navigating Regulatory Requirements and Guidelines
The storage and handling of vaccines are subject to stringent regulations and guidelines established by national and international health organizations. In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides comprehensive guidance on vaccine storage and handling, often referencing manufacturers’ recommendations. Similarly, the World Health Organization (WHO) sets international standards. Compliance with these guidelines is not optional; it is a legal and ethical obligation for all entities involved in vaccine administration. These regulations often specify:
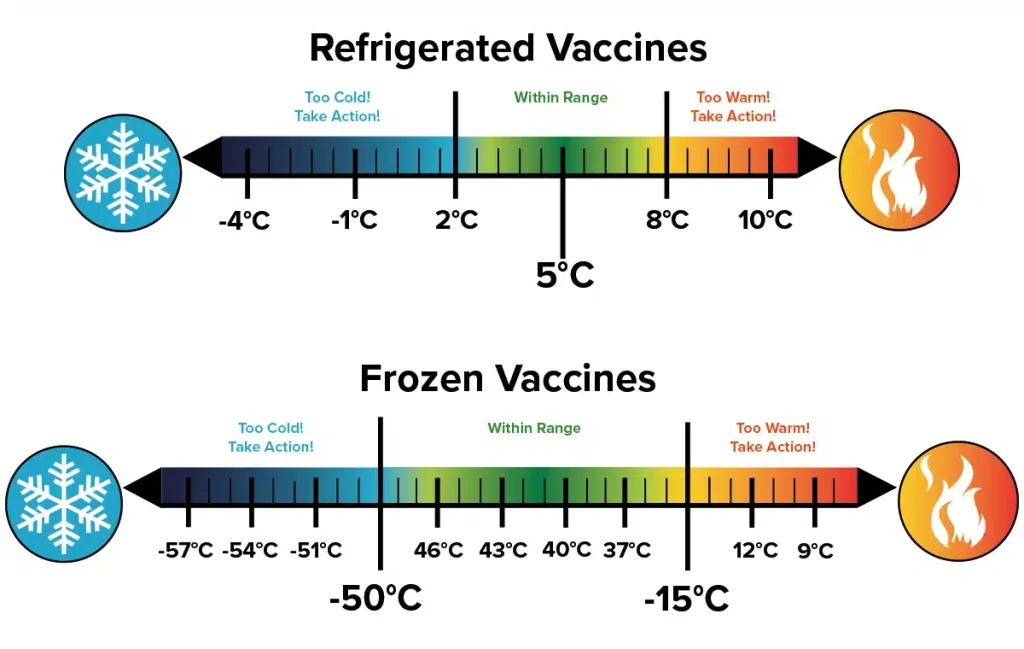
- Acceptable Temperature Ranges: Clearly defined temperature ranges for vaccine storage (typically 2°C to 8°C for refrigerated vaccines and specific ranges for frozen vaccines).
- Temperature Monitoring Requirements: The frequency and methods of temperature monitoring, including the use of calibrated thermometers and data loggers.
- Alarm System Requirements: The types of alarms required and the protocols for responding to temperature excursions.
- Storage Unit Specifications: Guidelines on the type of refrigeration units suitable for vaccine storage, explicitly discouraging the use of domestic refrigerators due to their inherent temperature variability.
- Inventory Management: Best practices for organizing and managing vaccine inventory to ensure proper rotation and prevent wastage.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: Requirements for maintaining detailed records of temperature logs, maintenance activities, and any temperature excursions.


Staying abreast of the latest regulatory updates and adhering meticulously to these guidelines is paramount for ensuring vaccine efficacy, patient safety, and avoiding potential penalties or legal repercussions.
Types of Vaccine Storage Refrigerators Available
The market offers various types of vaccine storage refrigerators to meet the diverse needs of different healthcare settings:
- Purpose-Built Pharmaceutical Refrigerators: These are specifically designed and engineered for the precise temperature control and stability required for vaccine storage. They often feature advanced temperature control systems, forced-air circulation, and comprehensive monitoring capabilities. These are generally considered the gold standard for vaccine storage.
- Medical-Grade Refrigerators: Similar to pharmaceutical refrigerators, medical-grade units are designed for the storage of medical supplies and often meet stringent temperature control requirements. They may offer a balance between performance and cost.
- Laboratory Refrigerators: These refrigerators are designed for scientific and laboratory applications and often provide excellent temperature uniformity and stability. Certain laboratory refrigerators can be suitable for vaccine storage, provided they meet the specific temperature requirements and have appropriate monitoring systems.
- Compact or Undercounter Refrigerators: These smaller units are suitable for settings with limited space or for storing smaller quantities of vaccines. However, it is crucial to ensure that even compact units offer precise temperature control and monitoring capabilities.
- Freezers for Frozen Vaccines: For vaccines that require frozen storage, specialized medical-grade freezers are essential. These freezers maintain ultra-low temperatures and have robust temperature monitoring and alarm systems.
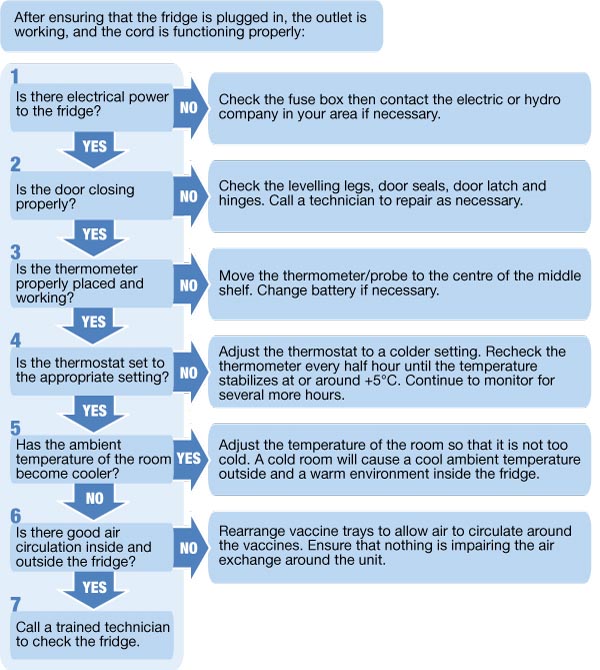
It is crucial to avoid using domestic refrigerators or freezers for vaccine storage. These units are not designed to maintain the consistent and narrow temperature ranges required for vaccines and often experience significant temperature fluctuations that can compromise vaccine potency.
Selecting the Right Vaccine Storage Refrigerator: Key Considerations
Choosing the appropriate vaccine storage refrigerator is a critical decision that requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Storage Capacity: Assess the volume of vaccines that need to be stored currently and consider future growth. Choose a refrigerator with sufficient capacity to accommodate your needs without overcrowding, which can impede air circulation.
- Temperature Stability and Uniformity: Prioritize refrigerators that demonstrate excellent temperature stability and uniformity throughout the cabinet. Look for units with forced-air circulation and robust temperature control systems.
- Monitoring and Alarm Systems: Ensure the refrigerator has a reliable digital temperature monitoring system with data logging capabilities and audible/visual alarms for temperature excursions, power failures, and door ajar situations.
- Compliance with Regulations: Verify that the refrigerator meets the relevant regulatory guidelines and standards set by your local and national health authorities (e.g., CDC, WHO).
- Reliability and Durability: Invest in a reputable brand known for producing reliable and durable medical-grade equipment. A dependable refrigerator will minimize the risk of unexpected failures and protect your valuable vaccine inventory.
- Maintenance Requirements: Consider the ease of maintenance and cleaning. Look for units with features that simplify these processes.
- Energy Efficiency: While temperature control is paramount, consider the energy efficiency of the refrigerator to minimize operating costs.
- Budget: Balance your needs and desired features with your budget. While it’s essential to invest in a quality unit, explore different options that meet your requirements.
Best Practices for Maintaining Your Vaccine Storage Refrigerator
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring the long-term performance and reliability of your vaccine storage refrigerator and the integrity of the vaccines stored within:
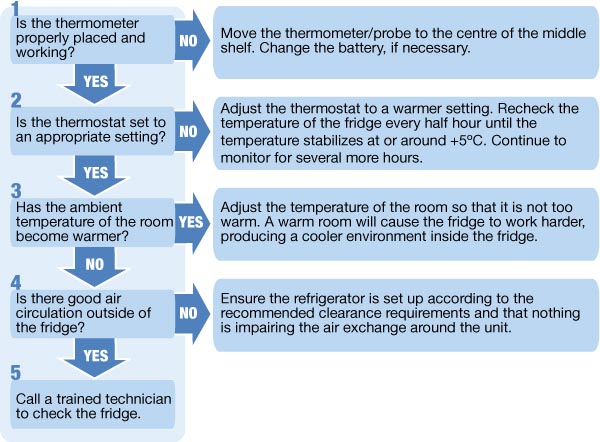
- Regular Temperature Monitoring: Implement a strict schedule for monitoring and recording refrigerator temperatures at least twice daily, or more frequently as recommended by guidelines. Use a calibrated thermometer separate from the unit’s internal display for accurate readings.
- Prompt Response to Alarms: Establish clear protocols for responding immediately to any temperature alarms. Investigate the cause of the alarm and take corrective action to restore the proper temperature range. Document all alarm events and the actions taken.
- Regular Cleaning: Clean the interior of the refrigerator regularly according to the manufacturer’s instructions to prevent the buildup of dust and debris, which can affect airflow and temperature uniformity.
- Preventative Maintenance: Schedule regular preventative maintenance checks by qualified technicians to ensure all components are functioning correctly. This may include checking door seals, fan motors, and cooling systems.
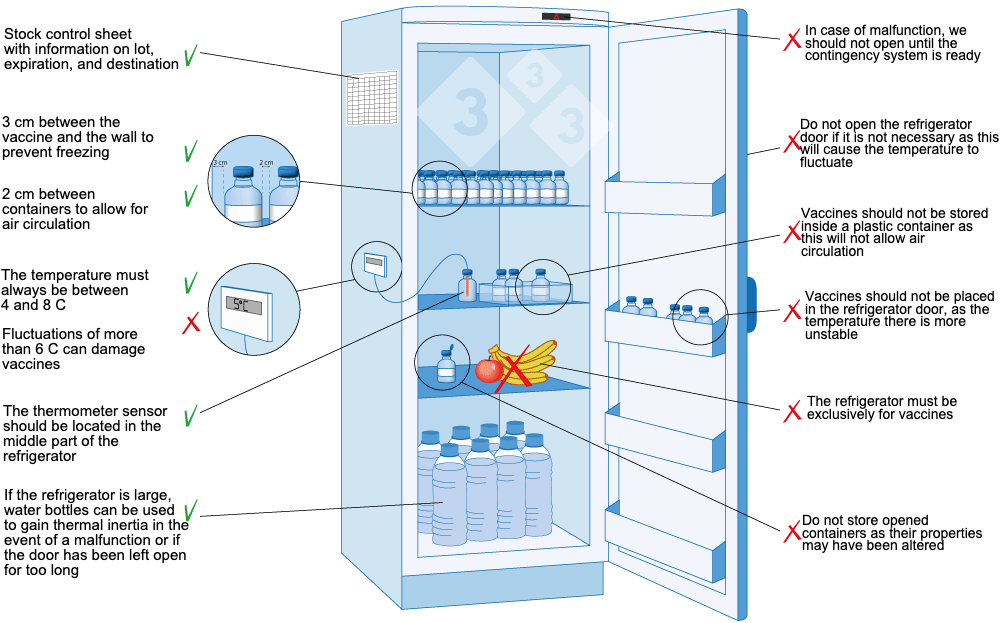
- Proper Loading and Storage: Organize vaccines within the refrigerator to allow for proper air circulation. Avoid overcrowding and ensure that vaccines are not placed directly against the walls or vents. Follow the “first-in, first-out” (FIFO) principle for inventory management.
- Avoid Storing Non-Vaccine Items: To minimize the risk of contamination and temperature fluctuations, dedicate the refrigerator solely to vaccine storage. Avoid storing food, beverages, or laboratory samples in the same unit.
- Keep Doors Closed: Minimize the frequency and duration of door openings to maintain a stable internal temperature. Ensure doors are always fully closed and seals are in good condition.
- Have a Backup Plan: Develop a contingency plan for vaccine storage in case of power outages or refrigerator malfunctions. This may involve having a backup generator or a designated alternative storage facility with appropriate temperature control.
Conclusion: Investing in Excellence for Vaccine Preservation
The vaccine storage refrigerator is more than just an appliance; it is a vital link in the cold chain, safeguarding the potency and efficacy of life-saving vaccines. By understanding the critical importance of proper storage, the key features of specialized refrigerators, the stringent regulatory landscape, and the best practices for maintenance, healthcare providers can make informed decisions and implement effective protocols to ensure the integrity of their vaccine supplies. Investing in a high-quality, purpose-built vaccine storage refrigerator and adhering to rigorous storage and handling procedures is not just a matter of compliance; it is a fundamental commitment to patient safety and public health. By prioritizing excellence in vaccine preservation, we can ensure that these essential medical interventions remain effective in protecting communities from preventable diseases. The long-term benefits of maintaining a robust cold chain through the use of reliable vaccine storage refrigerators far outweigh the initial investment, contributing to healthier populations and a more secure future for all.