In the intricate and critical world of pharmaceutical care, the meticulous management of medications is paramount. Among the various aspects of this management, pharmacy refrigeration stands out as a cornerstone, directly impacting the efficacy, safety, and ultimately, the well-being of patients. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the essential principles, regulatory frameworks, best practices, and technological advancements surrounding pharmacy refrigeration, providing an indispensable resource for pharmacists, pharmacy technicians, healthcare professionals, and anyone involved in the storage and handling of temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals.
The Critical Importance of Precise Temperature Control in Pharmacies
Many medications, including vaccines, insulin, biologics, and certain oral and injectable formulations, are inherently sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Exposure to temperatures outside their specified storage ranges can lead to irreversible degradation, loss of potency, and even the formation of harmful byproducts. This not only renders the medication ineffective but can also pose significant risks to patient health. Therefore, establishing and maintaining a robust and reliable pharmacy refrigeration system is not merely a matter of best practice; it is a fundamental requirement for ensuring the integrity and safety of the pharmaceutical supply chain within a pharmacy setting.
The consequences of inadequate refrigeration can be severe, ranging from reduced therapeutic effect and treatment failure to adverse drug reactions and loss of public trust. Furthermore, regulatory bodies worldwide impose stringent guidelines on the storage of temperature-sensitive medications, making compliance with these regulations a legal and ethical imperative for all pharmacies.

Understanding the Regulatory Landscape of Pharmacy Refrigeration
Navigating the complex web of regulations governing pharmacy refrigeration is crucial for any pharmacy operation. While specific requirements may vary slightly between jurisdictions, several overarching principles and guidelines are consistently emphasized. In many regions, adherence to standards set forth by organizations like the United States Pharmacopeia (USP), particularly USP General Chapter “Good Storage and Distribution Practices for Drug Products” and USP General Chapter “Storage and Handling of Investigational Drug Products”, is mandatory or strongly recommended. These chapters provide detailed guidance on temperature monitoring, equipment qualification, storage unit maintenance, and documentation practices.

Key regulatory considerations often include:
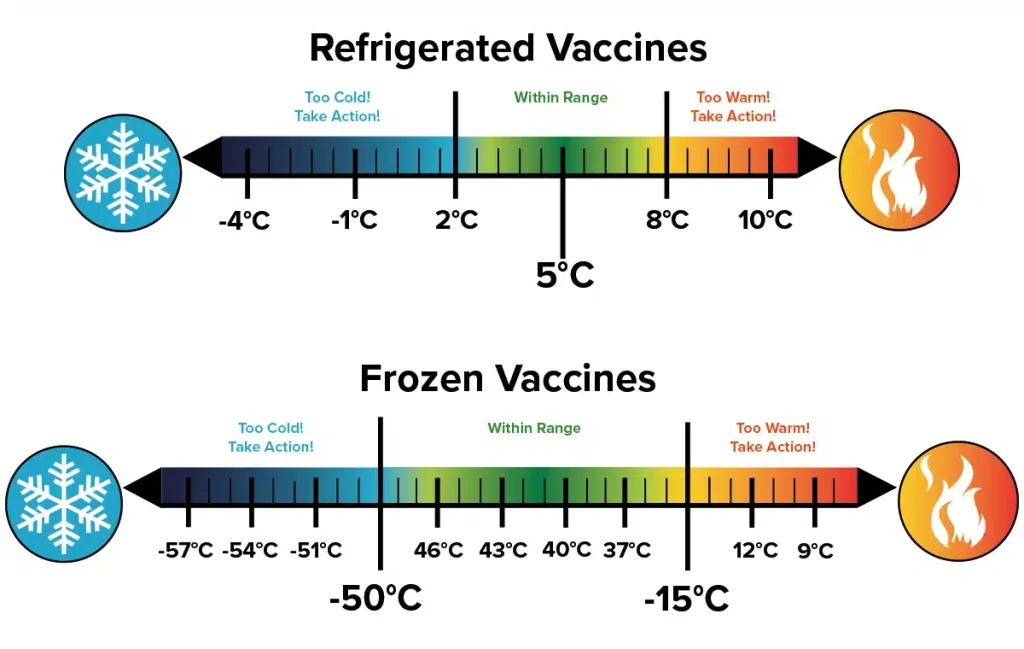
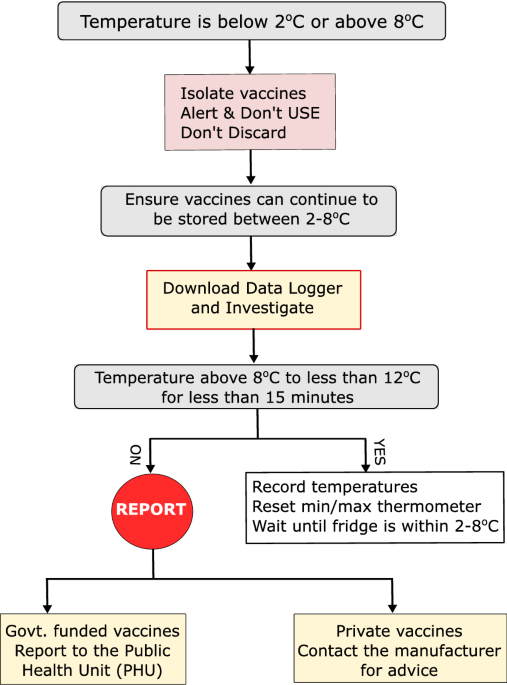
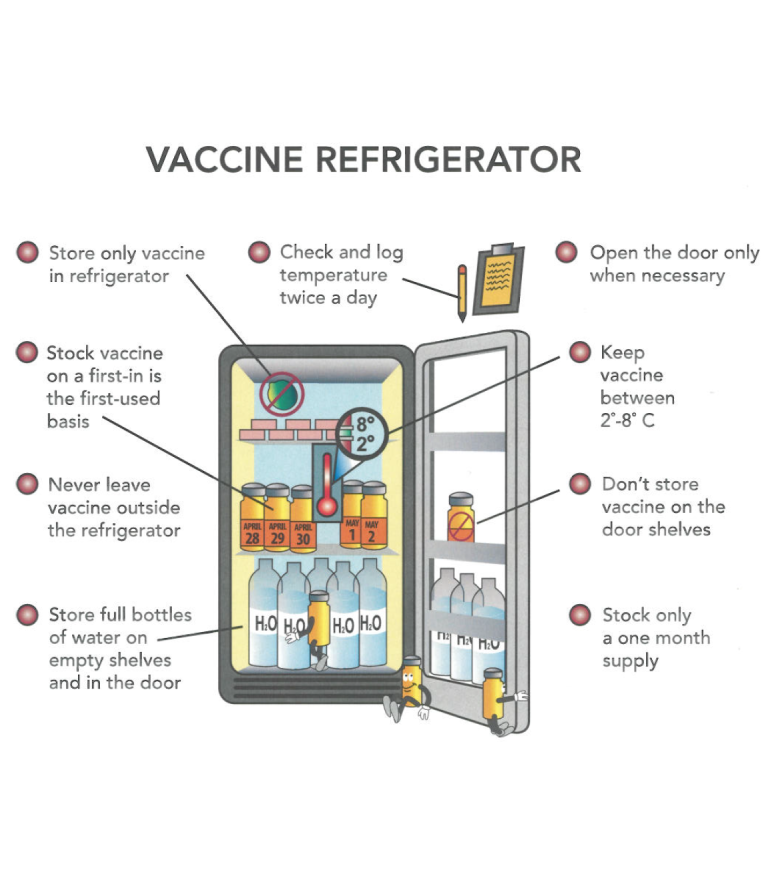
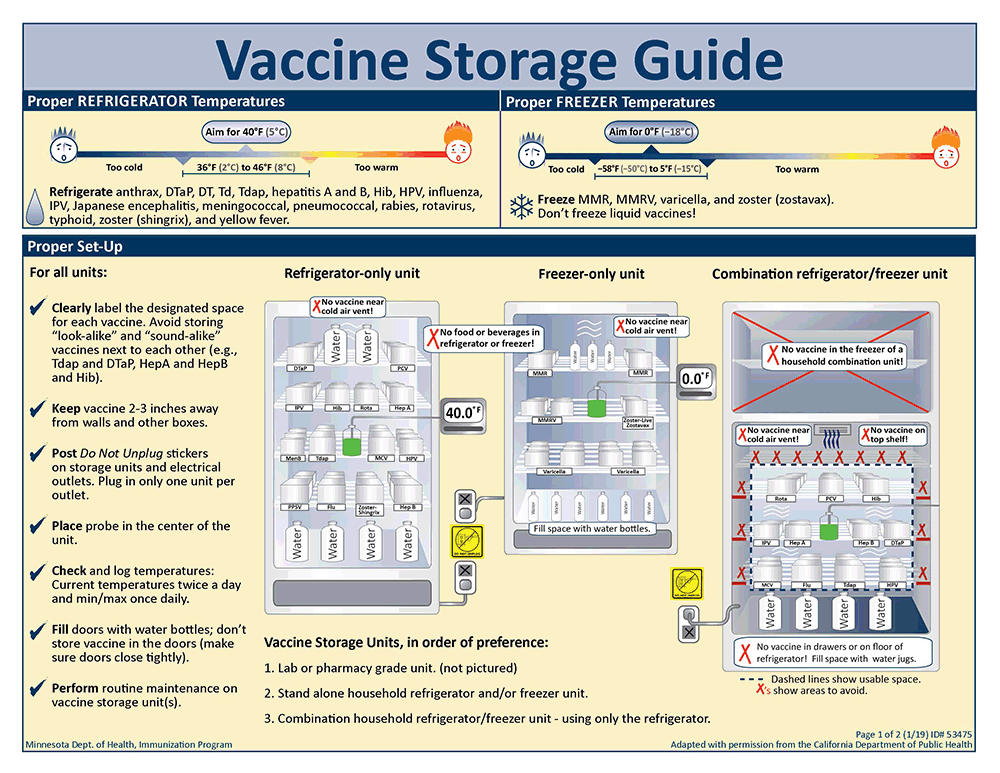
- Temperature Ranges: Clearly defined and strictly maintained temperature ranges for refrigerated (typically 2°C to 8°C or 36°F to 46°F) and frozen (typically -25°C to -10°C or -13°F to 14°F) medications.
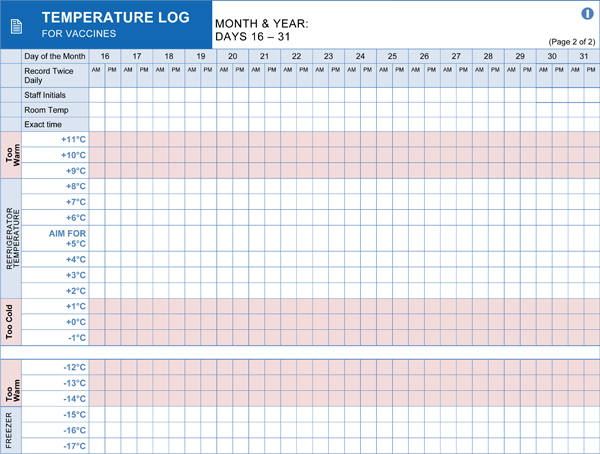
- Temperature Monitoring: Continuous and accurate temperature monitoring using calibrated devices, with regular recording and review of temperature logs.
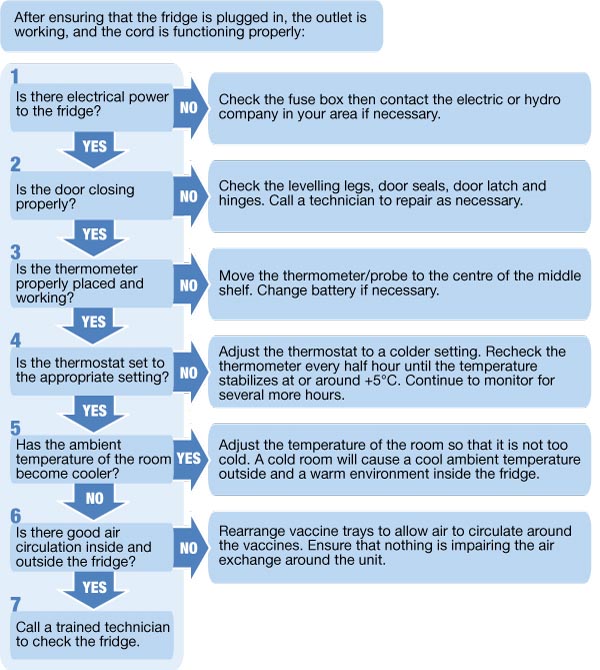
- Alarm Systems: Reliable alarm systems that provide immediate notification of temperature excursions outside the acceptable range.
- Equipment Qualification: Ensuring that pharmaceutical refrigerators and freezers are appropriately qualified (installation qualification, operational qualification, performance qualification) to consistently maintain the required temperature ranges.
- Storage Practices: Proper storage practices to ensure adequate air circulation, prevent overcrowding, and avoid temperature stratification within the unit.
- Documentation: Meticulous record-keeping of temperature logs, maintenance activities, calibration records, and any temperature excursions and corrective actions taken.

Staying abreast of the latest regulatory updates and guidelines is essential for maintaining compliance and ensuring patient safety.
Selecting the Right Pharmaceutical Refrigeration Equipment
Choosing the appropriate pharmaceutical refrigerators and freezers is a critical decision that directly impacts the pharmacy’s ability to maintain medication integrity. Standard household refrigerators are generally not suitable for pharmaceutical storage due to their inconsistent temperature control, lack of adequate monitoring capabilities, and potential for temperature fluctuations. Instead, pharmacies should invest in purpose-built medical-grade refrigerators and freezers designed specifically for the stringent requirements of pharmaceutical storage.
Key features to consider when selecting pharmacy refrigeration equipment include:
- Precise Temperature Control: Look for units with advanced temperature control systems that can maintain stable and uniform temperatures throughout the storage compartment.
- Forced-Air Circulation: Refrigerators with forced-air circulation systems help to ensure even temperature distribution and rapid temperature recovery after door openings.
- Digital Temperature Displays: External digital displays provide a clear and continuous indication of the internal temperature.
- Min/Max Temperature Recording: The ability to record minimum and maximum temperatures reached between readings is crucial for identifying potential temperature excursions.
- Alarm Systems: Integrated audible and visual alarm systems that alert staff to temperature deviations are essential for timely intervention.
- Lockable Doors: Securely lockable doors help to prevent unauthorized access and maintain the integrity of the stored medications.
- Dedicated Pharmaceutical Design: Features such as adjustable shelving, specialized compartments, and optimized airflow are designed to meet the unique needs of pharmaceutical storage.
- Reliability and Durability: Investing in high-quality, reliable equipment minimizes the risk of breakdowns and ensures long-term performance.

Consider the volume of medications requiring refrigeration, the available space, and the specific temperature requirements of the medications being stored when making equipment selection decisions.
Implementing Best Practices for Pharmacy Refrigerator Management
Simply having the right equipment is not enough; proper management and maintenance are equally crucial for ensuring the effectiveness of pharmacy refrigeration systems. Implementing robust standard operating procedures (SOPs) is essential for consistent and compliant practices.
Key best practices for pharmacy refrigerator management include:
- Regular Temperature Monitoring: Implementing a schedule for routine temperature checks and recording, at least twice daily (morning and evening), and ideally more frequently.
- Accurate Documentation: Maintaining detailed and accurate temperature logs, maintenance records, calibration certificates, and records of any temperature excursions and corrective actions.
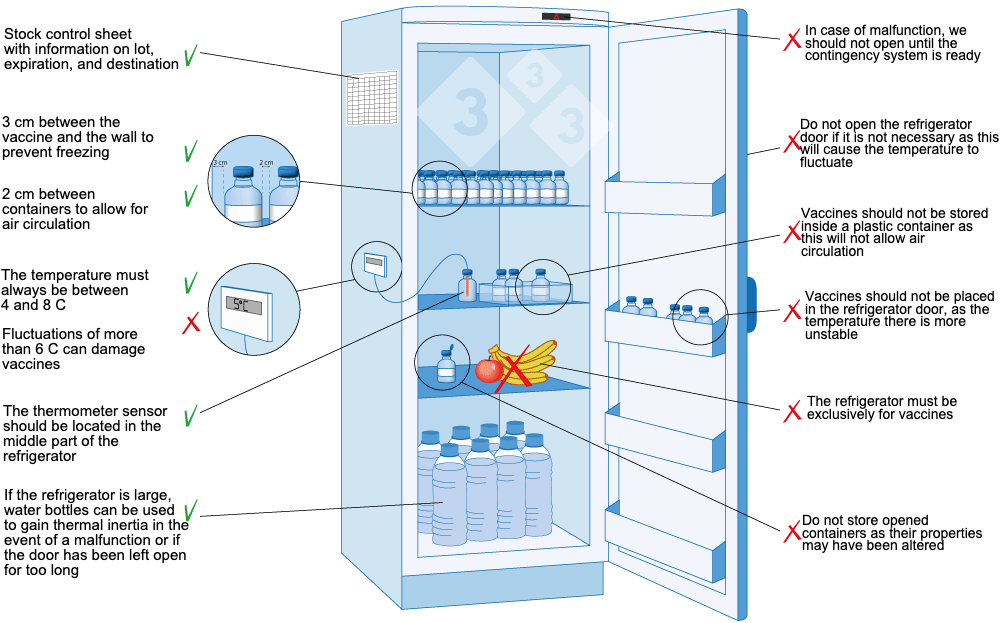
- Proper Loading and Storage: Ensuring adequate spacing between items to allow for proper air circulation and avoiding overcrowding the refrigerator. Medications should not be placed directly against the walls or near the air vents.
- Regular Cleaning and Maintenance: Establishing a schedule for routine cleaning of the interior and exterior of the refrigerators to prevent the buildup of dust and debris, which can affect performance. Regular maintenance checks should also be performed according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
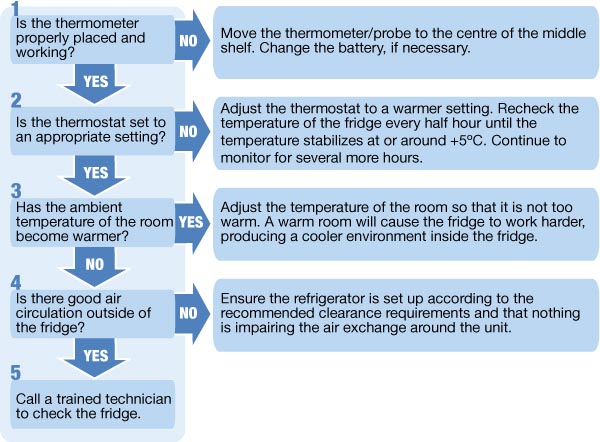
- Prompt Action on Temperature Excursions: Developing and implementing a clear protocol for addressing temperature excursions, including identifying the cause, isolating affected medications, and documenting the incident and any corrective actions taken.
- Staff Training: Providing comprehensive training to all pharmacy staff on the proper procedures for handling, storing, and monitoring refrigerated medications, as well as how to respond to temperature alarms.
- Calibration of Temperature Monitoring Devices: Ensuring that all temperature monitoring devices are regularly calibrated to maintain accuracy.
- Emergency Preparedness: Developing contingency plans for power outages or equipment failures to ensure the continued integrity of refrigerated medications. This may include having backup power sources or designated temporary storage solutions.
Adherence to these best practices will significantly contribute to maintaining the quality and safety of refrigerated medications and ensuring regulatory compliance.
The Role of Temperature Monitoring Systems in Modern Pharmacies
Advancements in technology have led to the development of sophisticated temperature monitoring systems that offer significant advantages over manual temperature logging. These systems often provide continuous, real-time temperature monitoring, automated data logging, and immediate alerts in the event of temperature excursions. Implementing such systems can enhance efficiency, improve accuracy, and reduce the risk of human error.
Features of advanced temperature monitoring systems may include:
- Wireless Sensors: Sensors placed within the refrigerators and freezers transmit temperature data wirelessly to a central monitoring system.
- Real-Time Data Logging: Temperature data is automatically logged at pre-defined intervals, providing a comprehensive audit trail.
- Automated Alerts and Notifications: The system can send immediate alerts via email, SMS, or other methods when temperatures deviate outside the acceptable range.
- Cloud-Based Data Storage and Access: Data is securely stored in the cloud, allowing for remote access and analysis.
- Reporting and Analytics: The system can generate reports and analytics to identify trends and potential issues.
- Integration with Building Management Systems: Some systems can be integrated with existing building management systems for centralized monitoring and control.

While the initial investment in a sophisticated temperature monitoring system may be higher, the long-term benefits in terms of efficiency, accuracy, and risk mitigation can be substantial.
Maintaining the Integrity of the Cold Chain in Pharmacy Operations
Pharmacy refrigeration is a critical link in the cold chain, which encompasses the entire process of transporting, storing, and handling temperature-sensitive products within a specified temperature range. Maintaining the integrity of the cold chain within the pharmacy setting is essential to ensure that medications remain safe and effective from the moment they are received until they are dispensed to the patient.

Key considerations for maintaining the cold chain within the pharmacy include:
- Proper Receiving Procedures: Verifying the temperature of incoming shipments of refrigerated medications upon arrival and documenting any discrepancies.
- Immediate Storage: Promptly transferring refrigerated medications to the designated pharmaceutical refrigerators upon receipt.
- Controlled Dispensing: Ensuring that refrigerated medications are dispensed to patients with appropriate instructions for storage and handling.
- Transportation (if applicable): If refrigerated medications need to be transported outside the pharmacy (e.g., for home healthcare), using validated transport containers and maintaining the required temperature range during transit.
Every step in the handling of refrigerated medications within the pharmacy must be carefully managed to preserve the cold chain and prevent temperature excursions.
Conclusion: The Indispensable Role of Pharmacy Refrigeration
In conclusion, pharmacy refrigeration is far more than just storing medications in a cool place. It is a complex and critical process that demands meticulous attention to detail, adherence to stringent regulations, and the implementation of best practices. By investing in appropriate equipment, implementing robust monitoring systems, and ensuring thorough staff training, pharmacies can safeguard the integrity of temperature-sensitive medications, protect patient health, and maintain regulatory compliance. The unwavering commitment to effective pharmacy refrigeration is an indispensable element of providing high-quality pharmaceutical care and upholding the trust placed in the pharmacy profession. The principles and practices outlined in this comprehensive guide serve as a vital framework for achieving and maintaining excellence in pharmacy refrigeration.