Maintaining the integrity of vaccines through proper storage is paramount to the success of immunization programs and the protection of public health. This comprehensive guide delves into the critical aspects of vaccine storage in freezers, providing in-depth information on temperature requirements, essential best practices, the selection and maintenance of appropriate equipment, and the fundamental scientific principles that underpin the need for stringent cold chain management. Understanding and adhering to these guidelines is not merely a recommendation; it is a necessity for ensuring that every administered vaccine is potent and effective.
The Crucial Role of Freezer Storage in Maintaining Vaccine Potency
Certain vaccines are exceptionally sensitive to temperature fluctuations and require storage at ultra-low or frozen temperatures to maintain their stability and efficacy. Deviations from these strict temperature ranges can lead to irreversible damage, rendering the vaccine ineffective and potentially compromising the health of the individuals receiving it. The process of vaccine storage in freezers is therefore a cornerstone of the cold chain, a temperature-controlled supply chain that begins with the manufacturer and extends to the point of administration. Any break in this chain can have significant consequences.

- Preserving Biological Integrity: Freezing temperatures significantly slow down or halt the biochemical reactions that can degrade the active components of a vaccine, such as antigens and adjuvants.
- Extending Shelf Life: Proper freezer storage is often essential for maximizing the shelf life of certain vaccines, allowing for efficient distribution and administration.
- Preventing Contamination: While not the primary purpose, maintaining vaccines in a controlled, clean freezer environment helps minimize the risk of microbial contamination.
Ignoring the specific storage requirements for vaccines that necessitate freezer conditions can lead to the administration of compromised products, resulting in inadequate immune responses and a false sense of security against preventable diseases. This underscores the critical importance of meticulous adherence to established protocols for vaccine storage in freezers.
Understanding Temperature Requirements for Freezer-Stored Vaccines
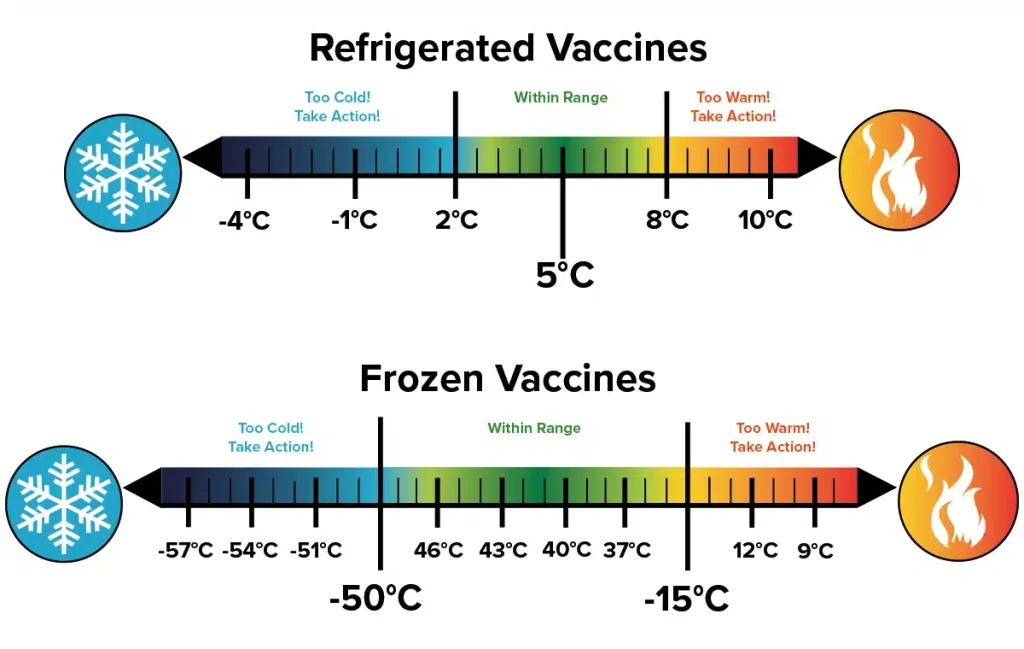
Not all vaccines require the same storage conditions. It is absolutely crucial to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and the specific recommendations of relevant public health authorities for each individual vaccine. However, for vaccines requiring freezer storage, there are general temperature ranges that must be strictly maintained.
- Ultra-Low Temperature Freezers (ULT): Some advanced mRNA vaccines, for instance, require storage at ultra-low temperatures, typically ranging from -80°C to -60°C (-112°F to -76°F). These specialized freezers are essential for maintaining the stability of these highly sensitive formulations.
- Standard Freezer Temperatures: Other vaccines may require storage in standard freezers, generally within the range of -25°C to -15°C (-13°F to 5°F). Again, it is imperative to verify the specific temperature requirements for each vaccine.
The use of incorrect freezer temperatures can have devastating consequences for vaccine potency. Storing a vaccine below its recommended minimum temperature can also be detrimental, potentially altering its composition or leading to physical damage. Therefore, precise temperature monitoring and control are non-negotiable aspects of effective vaccine storage in freezers.
Essential Best Practices for Effective Vaccine Storage in Freezers
Beyond simply placing vaccines in a freezer, a set of rigorous best practices must be implemented to ensure their continued efficacy and safety. These practices encompass everything from equipment selection to daily monitoring and emergency preparedness.
- Dedicated Pharmaceutical-Grade Freezers: Whenever possible, vaccines should be stored in freezers specifically designed for pharmaceutical or medical use. These freezers offer superior temperature control, stability, and monitoring capabilities compared to standard household or commercial freezers.
- Temperature Monitoring: Continuous temperature monitoring is paramount. This involves using calibrated data loggers or temperature probes with alarms that can alert staff to any temperature excursions outside the acceptable range. Manual temperature readings should also be taken and documented at least twice daily.
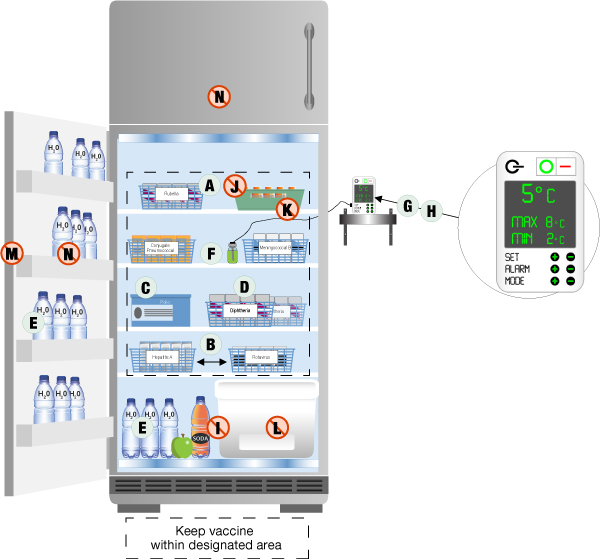
- Proper Air Circulation: Vaccines should be arranged within the freezer in a manner that allows for adequate air circulation. Overcrowding can lead to uneven temperature distribution. Leave space between boxes and avoid placing them directly against the freezer walls.
- Inventory Management: Implement a robust inventory management system, such as “first-expired, first-out” (FEFO), to ensure that vaccines are used before their expiration dates and to minimize the risk of wastage.
- Regular Maintenance: Freezers require regular maintenance, including defrosting (for non-frost-free models), cleaning, and inspection of door seals. Any signs of malfunction should be addressed immediately by qualified technicians.
- Emergency Preparedness: Develop and regularly practice a comprehensive emergency plan to address potential power outages or freezer malfunctions. This plan should include procedures for transferring vaccines to alternative storage or utilizing backup power sources.
- Staff Training: All personnel involved in the handling and storage of vaccines must receive thorough and ongoing training on proper procedures, including temperature monitoring, inventory management, and emergency protocols.
- Accurate Documentation: Maintain meticulous records of temperature logs, inventory, maintenance activities, and any temperature excursions. This documentation is crucial for accountability and regulatory compliance.
Adherence to these best practices forms the bedrock of a reliable system for vaccine storage in freezers, safeguarding the integrity of these vital medical products.
Selecting and Maintaining the Right Freezer Equipment
The choice of freezer is a critical decision that directly impacts the ability to maintain the required temperature range for stored vaccines. Several factors should be considered when selecting freezer equipment.
- Temperature Range and Stability: Ensure the freezer is capable of consistently maintaining the specific temperature range required for the vaccines being stored. Look for models with excellent temperature stability and uniformity.
- Storage Capacity: Select a freezer with adequate storage capacity to accommodate current and anticipated vaccine volumes without overcrowding.
- Monitoring and Alarm Systems: Opt for freezers equipped with integrated temperature monitoring systems and alarms that provide immediate notification of any temperature deviations. External data loggers can provide an independent record of temperature fluctuations.
- Reliability and Redundancy: Consider the reliability of the freezer and explore options for backup power or redundant freezer units, especially for ultra-low temperature storage where even brief temperature excursions can be critical.
- Maintenance Requirements: Evaluate the maintenance needs of different freezer models. Frost-free freezers can reduce the need for manual defrosting, but all units require regular inspection and cleaning.
Proper maintenance is just as important as selecting the right equipment. Regular checks of door seals, cleaning of condenser coils, and prompt repair of any malfunctions are essential for ensuring the long-term reliability and performance of freezers used for vaccine storage.
The Science Behind Freezer Storage: Maintaining Molecular Integrity
The need for vaccine storage in freezers stems from the inherent instability of certain biological molecules at higher temperatures. Vaccines often contain complex proteins, nucleic acids (like mRNA or DNA), and live or inactivated microorganisms. Elevated temperatures can lead to a variety of degradation processes, including:
- Protein Denaturation: Heat can cause proteins to unfold and lose their functional three-dimensional structure, rendering them ineffective as antigens.
- Nucleic Acid Degradation: Enzymes present in the vaccine or environmental factors can break down RNA or DNA molecules, compromising the vaccine’s ability to elicit an immune response.
- Loss of Viral or Bacterial Viability: For live-attenuated vaccines, higher temperatures can lead to a loss of the pathogen’s ability to replicate and stimulate immunity. For inactivated vaccines, it can further degrade the already non-viable organism.
- Aggregation and Precipitation: Temperature fluctuations can cause vaccine components to clump together or precipitate out of solution, affecting their stability and injectability.
By storing these sensitive biological materials at freezing temperatures, these degradation processes are significantly slowed down or effectively halted. The low temperatures reduce the kinetic energy of molecules, minimizing the rate of chemical reactions and preserving the structural and functional integrity of the vaccine components. This scientific principle underscores the absolute necessity of maintaining the correct freezer temperatures for specific vaccines to ensure their continued efficacy and safety upon administration.
Consequences of Improper Freezer Storage: A Public Health Risk
Failure to adhere to proper guidelines for vaccine storage in freezers carries significant risks, not only for individual patients but also for public health as a whole.
- Reduced Vaccine Potency: The most direct consequence is a decrease in the vaccine’s ability to elicit a protective immune response. Individuals who receive improperly stored vaccines may remain susceptible to the targeted disease.
- Need for Revaccination: When vaccine potency is compromised, individuals may need to be revaccinated, leading to increased costs, logistical challenges, and potential anxiety for patients.
- Erosion of Public Trust: Incidents of improperly stored vaccines can erode public confidence in immunization programs, potentially leading to decreased vaccination rates and increased risk of disease outbreaks.
- Wasted Resources: Discarding large quantities of temperature-compromised vaccines represents a significant financial loss and a waste of valuable resources.

Therefore, meticulous attention to every detail of vaccine storage in freezers is not just a matter of best practice; it is a fundamental responsibility for all stakeholders involved in the immunization process.
This comprehensive guide highlights the critical importance of proper vaccine storage in freezers. By understanding the temperature requirements, implementing best practices, selecting and maintaining appropriate equipment, and appreciating the underlying scientific principles, healthcare providers and public health officials can ensure the continued efficacy and safety of these life-saving medical interventions.