In the critical landscape of healthcare, the integrity of vaccines stands as a cornerstone of public health. The ability to effectively prevent and control infectious diseases hinges significantly on maintaining the potency and efficacy of these life-saving biological preparations. At the heart of this endeavor lies the indispensable role of specialized vaccine storage freezers. These are not merely standard refrigeration units; they are sophisticated, meticulously engineered systems designed to provide the precise and stable ultra-low temperatures required to preserve the delicate molecular structure of various vaccines.
Understanding the Critical Need for Specialized Freezers
Unlike conventional medications that may tolerate a broader range of storage conditions, vaccines are often highly sensitive biological products. Fluctuations in temperature, even minor and transient ones, can lead to irreversible degradation, rendering the vaccine ineffective and potentially unsafe. This underscores the paramount importance of investing in and diligently maintaining high-quality vaccine storage freezers that offer unparalleled temperature stability and reliability. Compromising on storage conditions is not an option; it directly jeopardizes the health and well-being of individuals and communities.

Exploring the Diverse Landscape of Vaccine Storage Freezer Types
The market offers a spectrum of vaccine storage freezer solutions, each tailored to meet specific needs and capacities. Understanding these different types is crucial for healthcare providers and institutions to make informed decisions:
- Ultra-Low Temperature (ULT) Freezers: These represent the gold standard for vaccines requiring extremely low temperatures, typically ranging from -86°C to -40°C. Often employing cascade refrigeration systems, ULT freezers provide exceptional temperature uniformity and stability, crucial for long-term storage of highly sensitive mRNA vaccines and other biologics.
- Deep Freezers: Operating in the temperature range of -40°C to -15°C, deep freezers offer a robust solution for vaccines requiring sub-zero storage but not the extreme temperatures of ULT freezers. They often feature single-compressor refrigeration systems and are available in various sizes and configurations.
- Cryogenic Freezers: Utilizing liquid nitrogen or mechanical refrigeration, cryogenic freezers achieve even lower temperatures, often below -150°C. While less common for routine vaccine storage, they may be employed for specialized research or long-term archival purposes.
- Benchtop Freezers: Compact and convenient, benchtop freezers are ideal for smaller clinics or laboratories with limited space and lower storage volume requirements. They offer reliable freezing capabilities within a smaller footprint.
- Plasma Freezers: While primarily designed for blood plasma storage, some plasma freezers can also be suitable for certain vaccines requiring temperatures around -30°C.
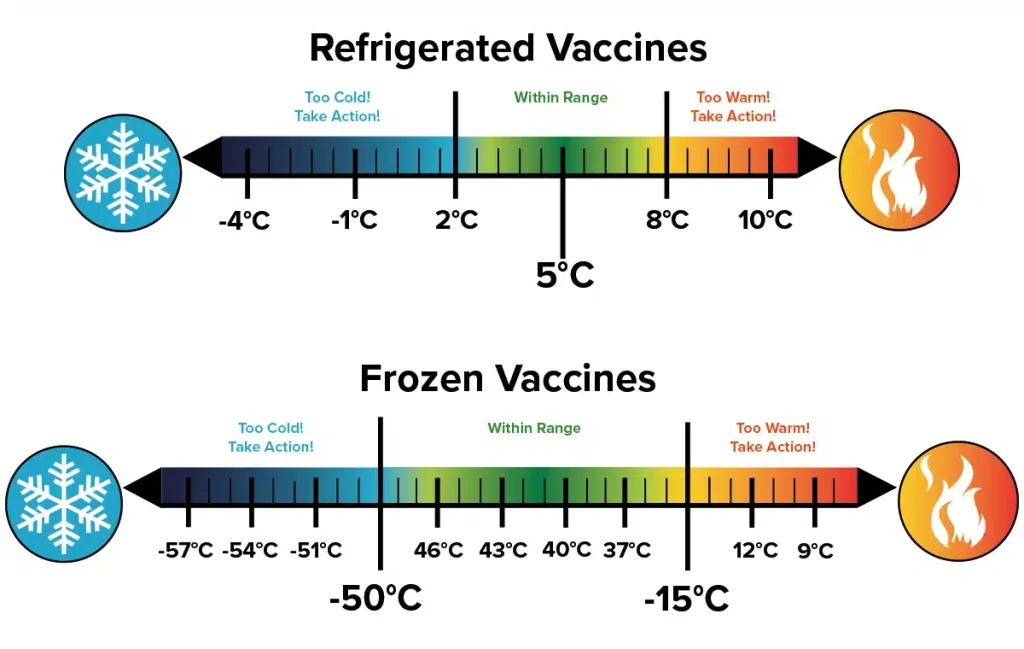
The selection of the appropriate vaccine storage freezer hinges on factors such as the specific temperature requirements of the vaccines being stored, the volume of vaccines, available space, and budgetary considerations.
Key Features and Technologies in Modern Vaccine Storage Freezers
Contemporary vaccine storage freezers are equipped with a range of advanced features and technologies designed to ensure optimal performance and safeguard vaccine integrity:
- Precise Temperature Control Systems: Microprocessor-based controllers with digital displays provide accurate and consistent temperature management, often with setpoint adjustability and alarm systems for temperature deviations.
- Advanced Insulation: High-quality insulation materials, such as vacuum insulation panels (VIPs) and polyurethane foam, minimize heat transfer, enhancing energy efficiency and temperature stability.
- Efficient Refrigeration Systems: Utilizing environmentally friendly refrigerants and optimized compressor designs, modern freezers offer powerful cooling capabilities while minimizing energy consumption.
- Temperature Monitoring and Recording: Integrated data loggers continuously monitor and record temperature fluctuations, providing a crucial audit trail for compliance and quality assurance. These systems often include audible and visual alarms for out-of-range temperatures.
- Alarm Systems: Comprehensive alarm systems alert users to critical events such as high/low temperature deviations, power failures, door ajar conditions, and sensor malfunctions. Remote alarm notification capabilities are increasingly common.
- Secure Access Control: Features like key locks or electronic access control systems help prevent unauthorized access to valuable vaccine supplies.
- Ergonomic Design: Features such as easy-to-open doors, adjustable shelving, and user-friendly interfaces contribute to efficient workflow and user comfort.
- Remote Monitoring Capabilities: Increasingly sophisticated systems allow for remote monitoring of freezer conditions, providing real-time data and alerts to designated personnel.
Investing in a vaccine storage freezer with these advanced features provides healthcare professionals with the confidence that their valuable vaccine inventory is being stored under optimal conditions.
Navigating Regulatory Landscapes and Compliance Standards
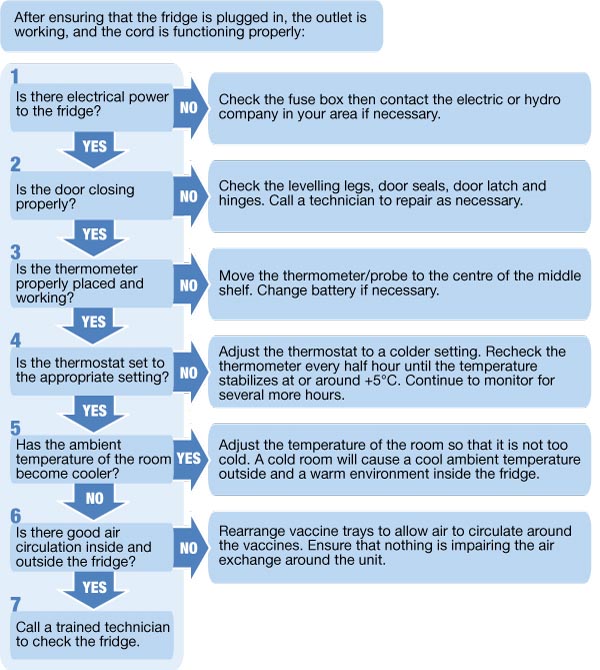
The storage of vaccines is subject to stringent regulations and guidelines established by national and international health organizations. Adherence to these standards is not merely a matter of compliance; it is fundamental to ensuring the safety and efficacy of vaccines administered to patients. Key regulatory bodies and guidelines include:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): The CDC provides comprehensive guidance on vaccine storage and handling, outlining temperature requirements, monitoring protocols, and best practices for maintaining the cold chain.
- World Health Organization (WHO): The WHO also issues detailed recommendations on vaccine storage and transportation, particularly relevant in a global context.
- National Immunization Programs: Individual countries often have their own specific regulations and guidelines that healthcare providers must adhere to.
- Pharmaceutical Industry Standards: Organizations like the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) provide standards for the storage and handling of pharmaceutical products, including vaccines.
Understanding and strictly adhering to these regulations is a non-negotiable aspect of vaccine management. Utilizing a vaccine storage freezer that meets or exceeds these standards is a crucial step in ensuring compliance and safeguarding public health.
Best Practices for Maintaining Your Vaccine Storage Freezer
Simply having a high-quality vaccine storage freezer is not enough. Consistent and diligent maintenance is essential to ensure its long-term reliability and performance. Key maintenance practices include:
- Regular Temperature Monitoring: Implement a robust temperature monitoring schedule, recording temperatures at least twice daily, or continuously using a data logger.
- Calibration of Temperature Monitoring Devices: Ensure the accuracy of temperature monitoring devices through regular calibration.
- Routine Cleaning: Regularly clean the interior and exterior of the freezer to prevent dust and ice buildup, which can affect performance.
- Defrosting (if manual): For freezers that are not frost-free, follow the manufacturer’s instructions for periodic defrosting to maintain efficiency.
- Preventing Overcrowding: Avoid overfilling the freezer, as this can impede air circulation and lead to uneven temperatures. Maintain adequate spacing between vaccine packages.
- Regular Inspection of Door Seals: Check door seals regularly for any signs of damage or wear, ensuring a tight seal to maintain temperature.
- Scheduled Professional Maintenance: Arrange for periodic professional servicing by qualified technicians to inspect and maintain the refrigeration system and other critical components.
- Proper Placement: Install the freezer in a well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight and heat sources, ensuring adequate clearance around the unit.
- Emergency Power Backup: Implement a contingency plan for power outages, including access to a reliable backup power source to maintain freezer operation.
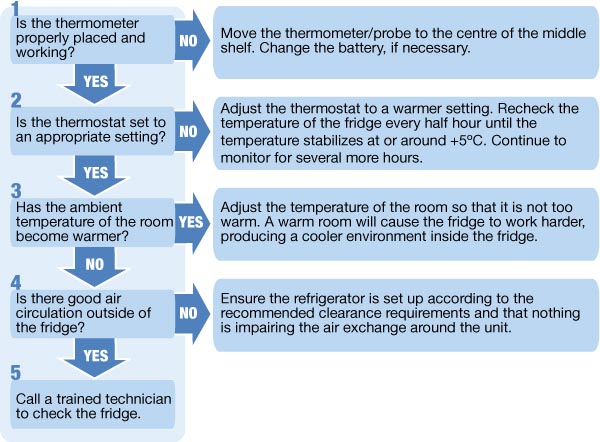
Adhering to these best practices will not only prolong the lifespan of your vaccine storage freezer but also ensure the continued integrity and efficacy of your valuable vaccine inventory.
The Future of Vaccine Storage Freezers: Innovations and Advancements

The field of vaccine storage is continuously evolving, with ongoing research and development focused on enhancing efficiency, sustainability, and reliability. Future trends and innovations may include:
- More Energy-Efficient Technologies: Development of freezers with lower energy consumption to reduce environmental impact and operating costs.
- Advanced Monitoring and IoT Integration: Integration with internet-of-things (IoT) platforms for real-time remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and enhanced data analytics.
- Improved Temperature Uniformity: Further advancements in airflow and refrigeration system design to ensure even more consistent temperatures throughout the freezer chamber.
- Sustainable Refrigerants: Transitioning to refrigerants with lower global warming potential.
- Smaller and More Portable Units: Development of more compact and portable freezer solutions for use in remote or resource-limited settings.
Staying informed about these advancements will enable healthcare providers to adopt the most effective and cutting-edge vaccine storage solutions in the future.
Conclusion: Investing in Excellence for Uncompromised Vaccine Integrity
In conclusion, vaccine storage freezers are indispensable assets in the healthcare ecosystem, playing a pivotal role in safeguarding the efficacy and safety of life-saving vaccines. Understanding the different types of freezers, their key features, relevant regulations, and best maintenance practices is crucial for healthcare professionals and institutions. By investing in high-quality vaccine storage freezers and adhering to stringent protocols, we can ensure the integrity of the cold chain, protect public health, and build a healthier future for all. The meticulous attention to detail in vaccine storage is not just a requirement; it is a commitment to the well-being of our communities and a testament to the unwavering dedication of healthcare professionals worldwide. The selection and maintenance of an appropriate vaccine storage freezer is a critical investment in this vital mission.





