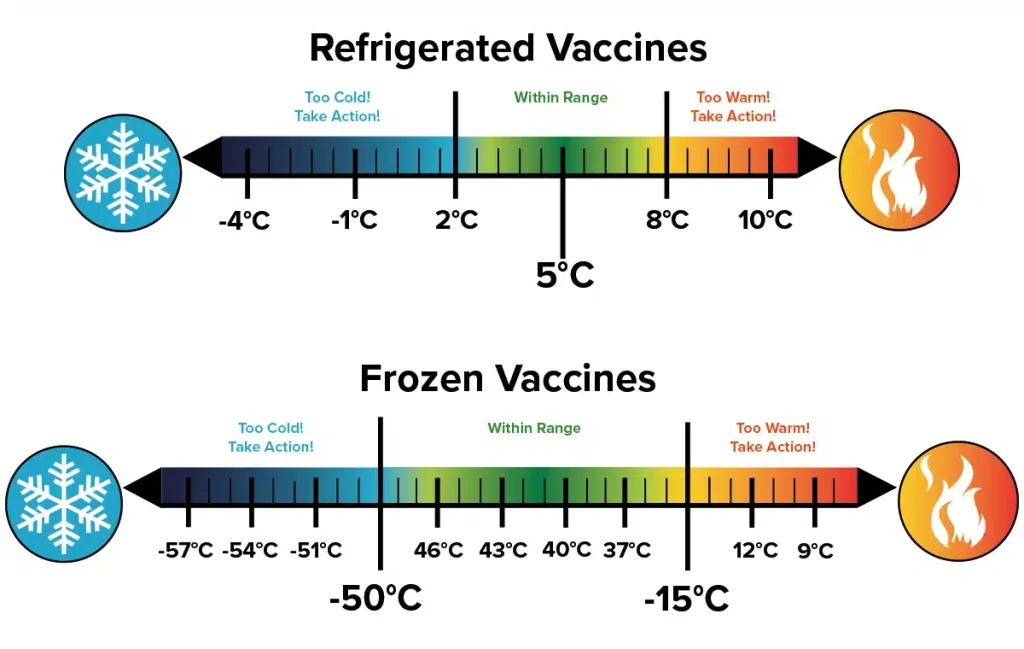
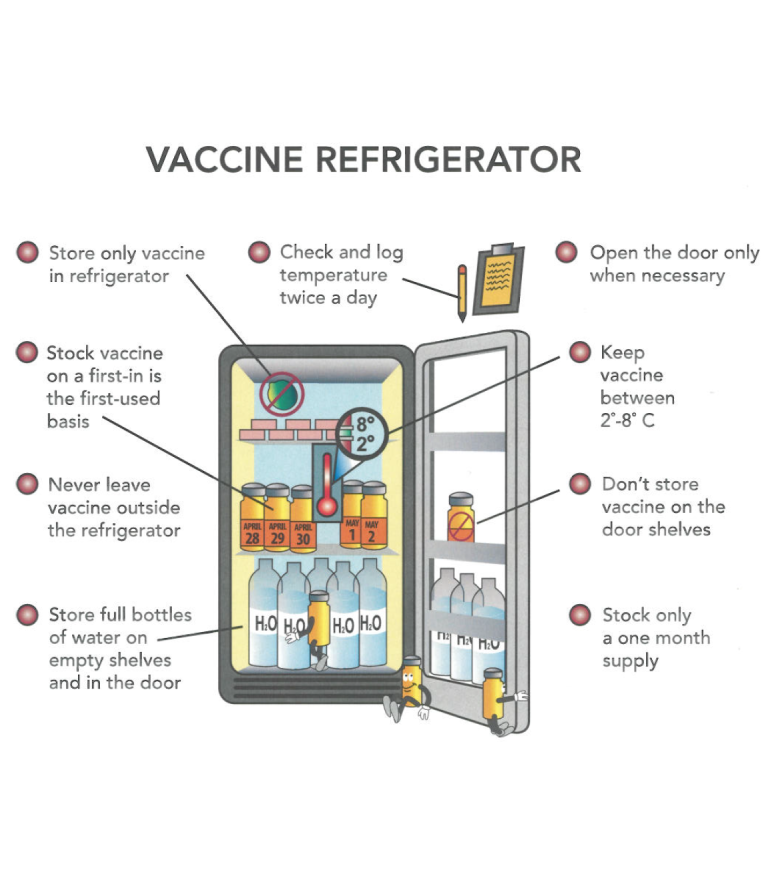
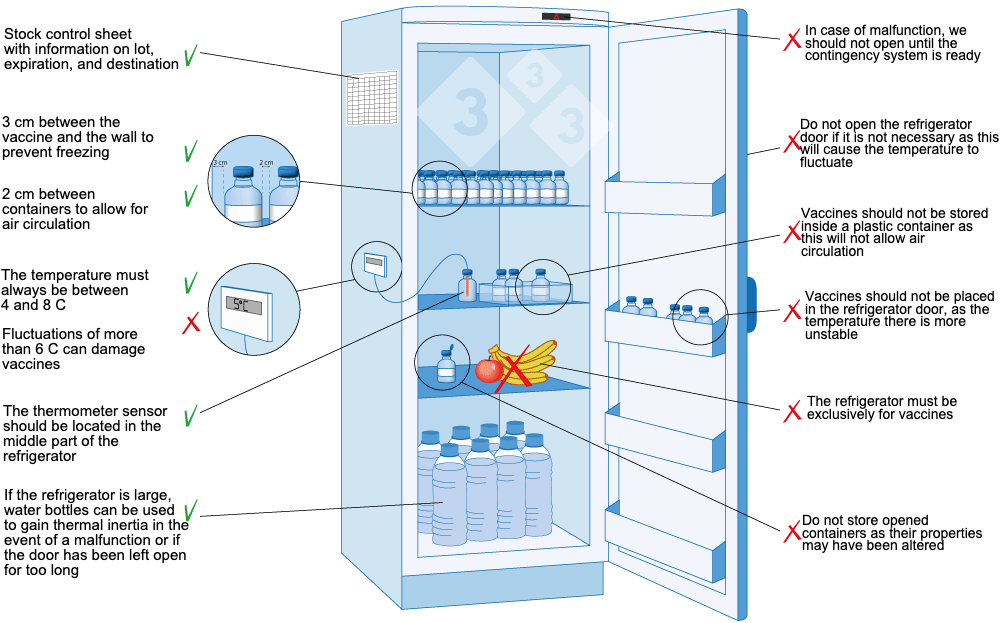
In the intricate and demanding realm of healthcare, the precise and reliable storage of temperature-sensitive materials is paramount. From life-saving vaccines and critical pharmaceuticals to delicate biological samples and vital blood components, the integrity of these substances directly impacts patient well-being and the efficacy of medical treatments. At the heart of this crucial process lies the medical refrigerator, a specialized piece of equipment meticulously engineered to maintain the stringent temperature conditions required for the safe and effective preservation of these essential medical supplies.
Understanding the Critical Role of Medical Refrigerators
Unlike standard household refrigerators, medical refrigerators are designed with a singular focus: unwavering temperature consistency and control. Fluctuations in temperature, even seemingly minor ones, can compromise the stability and potency of medications, vaccines, and biological specimens, rendering them ineffective or even harmful. Therefore, medical-grade refrigeration is not merely about keeping items cold; it’s about maintaining a precisely calibrated environment that adheres to rigorous industry standards and regulatory guidelines. The implications of inadequate storage can be severe, leading to wasted resources, compromised patient safety, and potential legal ramifications. This underscores the indispensable role of high-quality medical refrigeration solutions in every healthcare setting, from bustling hospitals and research laboratories to local pharmacies and private clinics.
Exploring the Diverse Landscape of Medical Refrigerator Types
The specific needs of different medical environments necessitate a diverse range of medical refrigerator types, each tailored to accommodate particular storage requirements and volumes. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for making informed decisions when selecting the appropriate equipment.
- Pharmaceutical Refrigerators: Primarily designed for the storage of medications and vaccines, these refrigerators often feature precise temperature control, digital displays with temperature monitoring, and alarm systems to alert personnel of any deviations from the setpoint. Many incorporate features like forced-air circulation for uniform temperature distribution and locking mechanisms for enhanced security.
- Vaccine Refrigerators: Given the delicate nature and strict temperature requirements of vaccines, these refrigerators are often engineered with even tighter temperature tolerances and more sophisticated monitoring systems. They may include features like dual temperature probes and data logging capabilities to ensure continuous and accurate record-keeping.
- Laboratory Refrigerators: Used for storing biological samples, reagents, and research materials, laboratory refrigerators often come in a variety of sizes and configurations, including under-counter, benchtop, and upright models. They may offer specialized features such as spark-free interiors for the storage of flammable materials and adjustable shelving for flexible storage options.
- Blood Bank Refrigerators: These highly specialized refrigerators are designed specifically for the storage of whole blood, blood components (such as plasma and platelets), and blood derivatives. They maintain very precise temperature ranges, often with continuous temperature monitoring and agitation systems to ensure the viability of the stored blood products. These units adhere to stringent regulatory requirements set forth by blood banking organizations.
- Ultra-Low Temperature (ULT) Freezers: While technically freezers, ULT units are often considered within the spectrum of medical cold storage due to their critical role in preserving highly sensitive biological samples and research materials at extremely low temperatures (typically -80°C or lower).
Key Features to Consider When Selecting a Medical Refrigerator
Choosing the right medical refrigerator involves careful consideration of several critical features that directly impact its performance, reliability, and suitability for your specific needs.
- Precise Temperature Control: The ability to accurately and consistently maintain the required temperature range is the most fundamental aspect of a medical refrigerator. Look for models with digital temperature controllers that allow for precise setpoint adjustments and minimal temperature fluctuations.
- Temperature Monitoring and Alarms: Real-time temperature monitoring and robust alarm systems are essential for ensuring the integrity of stored items. Features to look for include digital temperature displays, high/low temperature alarms (both audible and visual), and the ability to connect to external monitoring systems.
- Uniform Temperature Distribution: Consistent temperature throughout the refrigerator cabinet is crucial to prevent hot or cold spots that could compromise the stored materials. Forced-air circulation systems are often employed to achieve optimal temperature uniformity.
- Reliability and Durability: Medical refrigerators are critical investments that need to operate reliably for extended periods. Choose models from reputable manufacturers known for their quality construction and durable components.
- Security Features: Depending on the value and sensitivity of the stored items, security features such as locking doors and password protection for temperature settings may be necessary.
- Storage Capacity and Configuration: Select a refrigerator with sufficient storage capacity to accommodate your current and anticipated needs. Consider the internal configuration, including the number and adjustability of shelves, drawers, and compartments, to optimize organization and accessibility.
- Energy Efficiency: While performance is paramount, energy efficiency can contribute to long-term cost savings. Look for models with energy-efficient compressors and insulation.
- Compliance with Regulations: Ensure that the chosen medical refrigerator meets relevant industry standards and regulatory requirements, such as those set forth by healthcare organizations and government agencies.
- Ease of Maintenance: Features that simplify cleaning and maintenance, such as automatic defrost cycles and easily accessible components, can contribute to the longevity and optimal performance of the refrigerator.
- Data Logging Capabilities: For critical applications, the ability to log temperature data over time can be essential for compliance and quality control purposes. Some medical refrigerators offer built-in data loggers or the ability to connect to external data logging systems.
Navigating the Regulatory Landscape for Medical Refrigeration
The use of medical refrigerators is subject to stringent regulations and guidelines designed to ensure the safety and efficacy of stored medical supplies. These regulations may vary depending on the specific type of material being stored, the healthcare setting, and the governing authorities. It is crucial for healthcare professionals and facility managers to be thoroughly familiar with and adhere to these requirements. This includes maintaining accurate temperature logs, implementing proper storage protocols, and regularly calibrating and maintaining the refrigeration equipment. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant penalties and, more importantly, jeopardize patient safety. Understanding and adhering to guidelines from organizations such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the World Health Organization (WHO), and local health authorities is a non-negotiable aspect of managing medical cold storage.
Best Practices for Maintaining Your Medical Refrigerator
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring the long-term reliability and optimal performance of your medical refrigerator. Regular maintenance not only helps to prevent costly breakdowns but also ensures that the stored materials are consistently maintained within the required temperature range. Key maintenance practices include:
- Regular Cleaning: Clean the interior and exterior of the refrigerator regularly using appropriate cleaning solutions to prevent the build-up of dust, debris, and potential contaminants.
- Temperature Monitoring: Implement a consistent schedule for monitoring and recording the refrigerator’s temperature, even if the unit has an automatic data logging system. Manually checking the temperature provides an additional layer of verification.
- Defrosting (if manual): If your refrigerator has a manual defrost cycle, ensure that it is defrosted regularly to prevent excessive ice build-up, which can impair cooling efficiency and temperature uniformity.
- Checking Door Seals: Regularly inspect the door seals to ensure they are intact and creating a tight seal. Damaged or worn seals can lead to temperature fluctuations and increased energy consumption.
- Preventing Overcrowding: Avoid overpacking the refrigerator, as this can impede air circulation and lead to uneven temperature distribution. Ensure that there is adequate space between stored items.
- Regular Professional Servicing: Schedule regular professional servicing by qualified technicians to inspect and maintain the refrigerator’s mechanical and electrical components.
- Calibration: Periodically calibrate the temperature monitoring system to ensure its accuracy.
Making the Right Choice: Selecting a Medical Refrigerator for Your Needs

Selecting the ideal medical refrigerator requires a thorough assessment of your specific requirements, including the types and volumes of materials to be stored, the available space, budgetary constraints, and regulatory compliance obligations. By carefully considering the different types of medical refrigerators available, evaluating the key features, and understanding the importance of proper maintenance and regulatory adherence, you can make an informed decision that ensures the safe and effective storage of your critical medical supplies, ultimately contributing to बेहतर patient care and operational efficiency. Investing in a high-quality, reliable medical refrigerator is an investment in the integrity of your practice and the well-being of those you serve. The long-term benefits of precise temperature control, robust monitoring systems, and adherence to stringent standards far outweigh the initial cost, providing peace of mind and ensuring the efficacy of your valuable medical resources.