Ever wondered how much energy your refrigerator actually uses? You’re not alone! Understanding your fridge wattage consumption is crucial for managing your energy bills and making eco-friendly choices. Let’s break down the science behind it and explore practical ways to optimize your fridge’s power usage.
What is Wattage and Why Does it Matter?
Wattage, measured in watts (W), indicates the rate at which an appliance consumes energy. The higher the wattage, the more power it uses. Knowing your fridge’s wattage helps you estimate its energy consumption and calculate your electricity costs. It’s like knowing how much fuel your car uses per mile—essential for budgeting and planning!
Factors Affecting Fridge Wattage
Several factors influence a refrigerator’s wattage consumption:
- Size and Type: Larger fridges and those with features like ice makers and water dispensers generally consume more power.
- Age and Condition: Older fridges are often less energy-efficient than newer models. A faulty door seal or dirty condenser coils can also increase energy usage.
- Temperature Settings: Lower temperature settings require more energy to maintain.
- Ambient Temperature: In hotter climates, your fridge has to work harder to stay cool.
- Frequency of Door Openings: Each time you open the door, warm air enters, and the fridge uses extra energy to cool it down.
How to Calculate Your Fridge’s Wattage Consumption

To calculate your fridge’s energy usage, you need to know its wattage and how many hours it runs per day. You can find the wattage on the appliance’s label or in its user manual.
Here’s the formula:
Energy Consumption (kWh) = (Wattage × Hours Used Per Day) / 1000
For example, if your fridge has a wattage of 150W and runs for 12 hours a day:
Energy Consumption = (150W × 12 hours) / 1000 = 1.8 kWh per day

To get your monthly consumption, multiply the daily consumption by the number of days in the month.
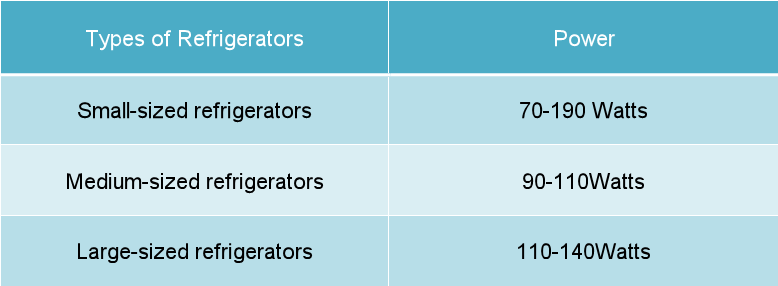
Common Fridge Wattage Ranges
Here’s a general idea of typical fridge wattage ranges:
- Small Fridges (e.g., mini-fridges): 50-100W
- Standard Top-Freezer Fridges: 100-250W
- Side-by-Side and French Door Fridges: 200-400W
Tips to Reduce Fridge Wattage Consumption
Want to lower your energy bills? Here are some practical tips:
- Maintain Proper Ventilation: Ensure there’s adequate space around your fridge for air circulation.
- Clean Condenser Coils: Regularly clean the coils at the back of your fridge to improve efficiency.
- Check Door Seals: Replace worn-out seals to prevent cool air from escaping.
- Adjust Temperature Settings: Set your fridge to the optimal temperature (around 37-40°F or 3-4°C) and your freezer to 0°F or -18°C.
- Avoid Overfilling: Overfilling can restrict airflow and make your fridge work harder.
- Let Hot Foods Cool: Allow hot foods to cool before placing them in the fridge.
- Consider an Energy-Efficient Model: If your fridge is old, consider upgrading to a newer, energy-efficient model.

The Impact of Energy-Efficient Fridges
Modern refrigerators are designed with energy efficiency in mind. Look for models with the Energy Star label, which indicates they meet strict energy-efficiency guidelines. These fridges often use advanced technologies like variable-speed compressors and improved insulation to minimize energy consumption.
By making informed choices about your fridge’s energy usage, you can significantly reduce your environmental footprint and save money on your electricity bills. It’s a win-win situation!
Conclusion
Understanding fridge wattage consumption is more than just a technical detail; it’s a step towards responsible energy usage. By monitoring and optimizing your fridge’s power consumption, you can contribute to a more sustainable future. Keep these tips in mind, and you’ll be well on your way to a more energy-efficient home.