In the intricate dance of food preservation, refrigeration stands as a cornerstone, a vital process that extends the life of our sustenance, safeguards our health, and minimizes the pervasive issue of food waste. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the science, art, and best practices of food refrigeration, providing you with the knowledge necessary to optimize your storage techniques, understand the nuances of different cooling technologies, and ultimately ensure the food you consume is not only delicious but also safe and nutritious. From the humble home refrigerator to sophisticated commercial cooling systems, mastering food refrigeration is an indispensable skill for anyone who handles, prepares, or consumes food.
Understanding the Fundamental Principles of Refrigeration
At its core, refrigeration is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space and transferring it elsewhere, thereby lowering the temperature within that space. This seemingly simple action has profound effects on the biological and chemical processes that lead to food spoilage. Microorganisms, such as bacteria, yeasts, and molds, thrive in warmer temperatures, multiplying rapidly and causing food to decay. Enzymes present within food also continue their activity, leading to changes in texture, flavor, and nutritional value. By significantly reducing the temperature, refrigeration effectively slows down these processes, extending the edible lifespan of a wide array of food items.
- Slowing Microbial Growth: Lower temperatures inhibit the reproduction and activity of spoilage-causing microorganisms.
- Retarding Enzymatic Activity: Refrigeration reduces the rate of enzymatic reactions that contribute to ripening, aging, and eventual degradation of food quality.
- Maintaining Moisture Levels: Proper refrigeration helps to maintain the appropriate humidity levels, preventing excessive drying or the accumulation of unwanted moisture that can promote spoilage.
Exploring Different Types of Refrigeration Technologies
The world of food refrigeration encompasses a diverse range of technologies, each designed to meet specific needs and scales of operation. Understanding these different types can help you make informed decisions about storage and preservation.
Home Refrigeration Systems
The standard household refrigerator typically utilizes a vapor-compression cycle. This involves a refrigerant circulating through a closed system, absorbing heat from inside the refrigerator and releasing it outside. Key components include the compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator. Modern refrigerators often come equipped with features like adjustable temperature zones, humidity control, and frost-free operation, further enhancing their ability to preserve different types of food optimally.

Commercial Refrigeration Solutions
Commercial settings, such as restaurants, supermarkets, and food processing plants, require robust and often specialized refrigeration systems. These can include walk-in coolers and freezers, display refrigerators, blast chillers (for rapidly cooling food), and specialized units for specific products like beverages or delicate produce. These systems are designed for high capacity, consistent temperature maintenance, and energy efficiency in demanding environments.
Other Refrigeration Methods
Beyond conventional mechanical refrigeration, other methods exist, although they may be less common for everyday food storage. These include:
- Evaporative Cooling: Utilizing the principle of evaporation to cool air, often used in arid climates for preserving fruits and vegetables.
- Cryogenic Freezing: Employing extremely low temperatures using liquid nitrogen or carbon dioxide for rapid freezing, which can result in superior texture and quality retention.
- Absorption Refrigeration: Using a heat source (like gas or solar energy) to drive the cooling process, often found in recreational vehicles or off-grid applications.
Mastering the Art of Food Storage in Your Refrigerator
Simply placing food in the refrigerator is not enough to guarantee optimal preservation. Proper organization and adherence to best practices are crucial for maximizing shelf life, preventing cross-contamination, and ensuring food safety.
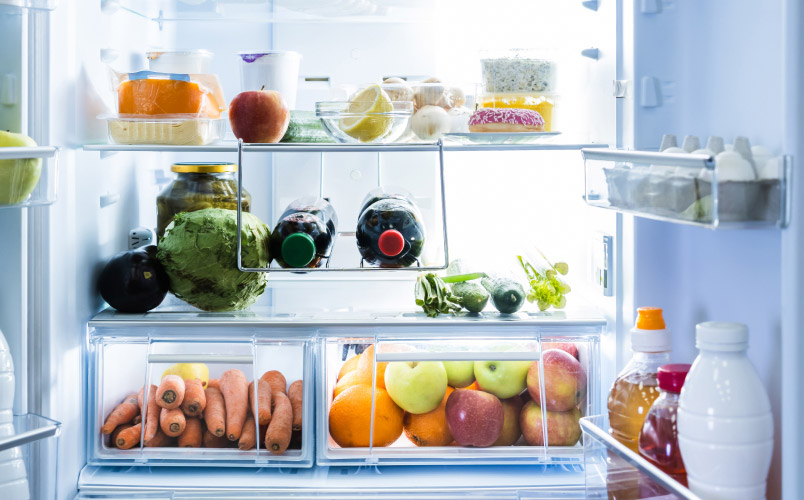
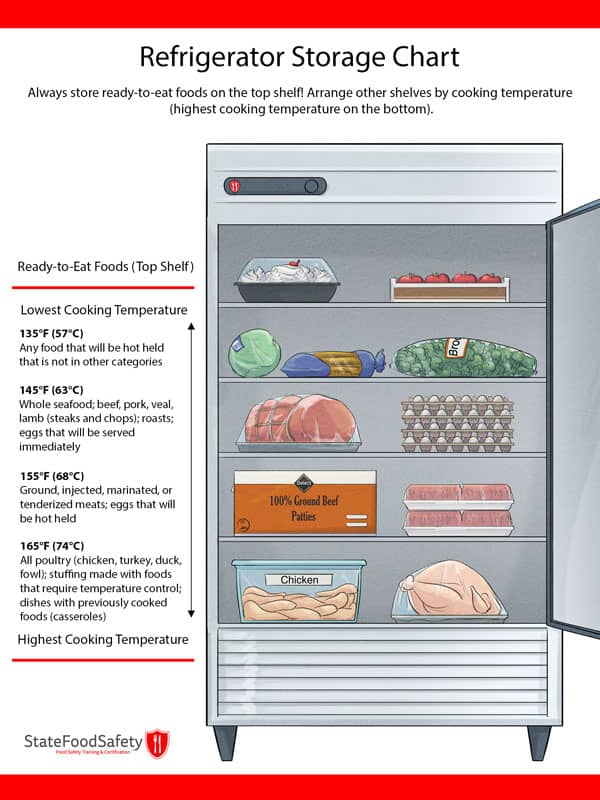
Temperature Zones and Placement
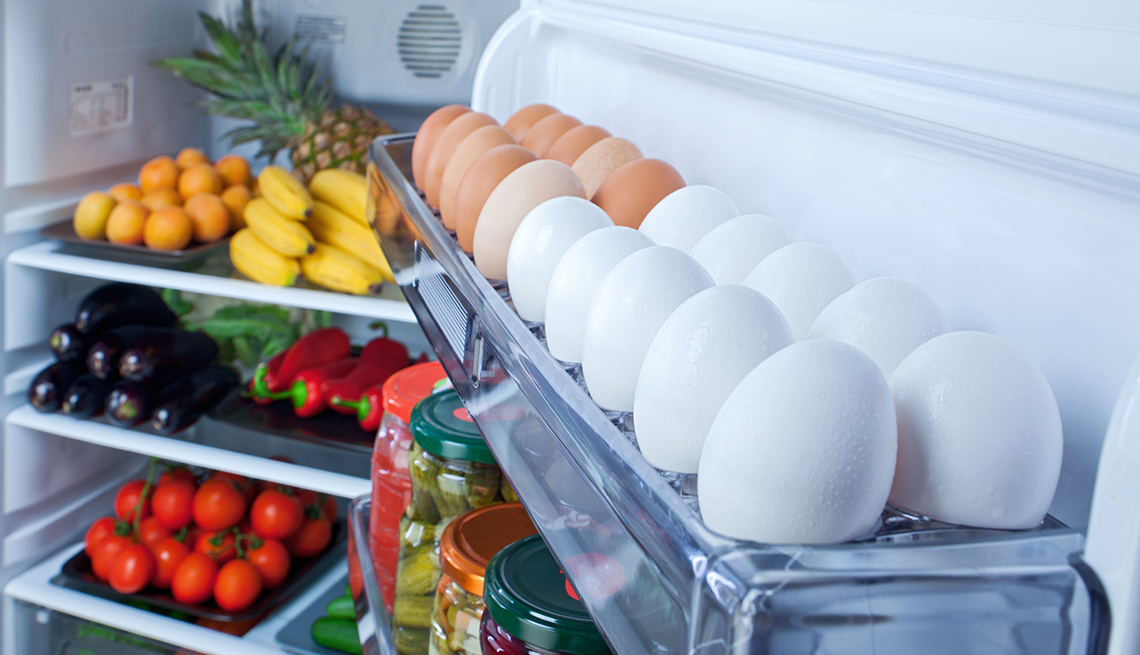
Refrigerators are not uniformly cold. Understanding the different temperature zones within your appliance is key to storing food correctly:
- Coldest Zone (Usually the Bottom Shelves and Back): Ideal for raw meats, poultry, and fish, as well as highly perishable items. This helps prevent bacterial growth and potential cross-contamination.
- Middle Shelves: Best for dairy products, cooked meats, and leftovers.
- Door Shelves: Generally the warmest part of the refrigerator and subject to temperature fluctuations. Suitable for less perishable items like condiments, jams, and some beverages. Avoid storing milk or eggs on the door.
- Crisper Drawers: Designed to maintain higher humidity levels, ideal for storing fruits and vegetables, helping to prevent wilting and moisture loss. Keep fruits and vegetables separate, as some fruits release ethylene gas, which can accelerate the spoilage of vegetables.


Best Practices for Food Storage
- Cool Food Before Refrigerating: Allowing hot food to cool to room temperature before placing it in the refrigerator prevents the internal temperature of the appliance from rising, which can compromise the safety of other stored items.
- Use Airtight Containers and Wraps: Properly wrapping or storing food in airtight containers helps to prevent moisture loss, odor transfer, and cross-contamination.
- Label and Date Leftovers: Clearly labeling leftovers with the date they were cooked helps you keep track of their freshness and avoid consuming spoiled food. Aim to consume leftovers within 3-4 days.
- Avoid Overcrowding: Overpacking the refrigerator can impede proper air circulation, leading to uneven cooling and potentially warmer spots where bacteria can thrive.
- Regular Cleaning: Regularly clean your refrigerator to remove spills and food debris, which can harbor bacteria and contribute to unpleasant odors.
- Check and Maintain Temperature: Ensure your refrigerator is set to the recommended temperature range (typically between 0°C and 4°C or 32°F and 40°F). Use a refrigerator thermometer to verify the internal temperature.
The Importance of Temperature Control and Food Safety
Temperature control is paramount in food refrigeration for ensuring food safety. The “danger zone,” between 4°C (40°F) and 60°C (140°F), is the temperature range where bacteria multiply most rapidly. Keeping food consistently below 4°C significantly slows down this growth, reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses. Understanding and adhering to safe refrigeration practices is not just about preserving quality; it’s about protecting your health and the health of others.
- Preventing Bacterial Growth: Maintaining cold temperatures inhibits the proliferation of harmful bacteria like Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria.
- Minimizing the Risk of Foodborne Illnesses: Proper refrigeration is a critical step in preventing food poisoning and related health issues.
- Maintaining Food Quality and Nutritional Value: While safety is the primary concern, consistent refrigeration also helps to retain the flavor, texture, and nutritional content of food for a longer period.
Extending Shelf Life: Refrigeration and Beyond
While refrigeration is a powerful tool for extending the shelf life of many foods, it’s often used in conjunction with other preservation methods for even longer storage:
- Freezing: Freezing food at temperatures below -18°C (0°F) effectively halts microbial growth and enzymatic activity, allowing for long-term storage.
- Canning: A process of preserving food in airtight containers by applying heat to kill microorganisms.
- Drying: Removing moisture from food to inhibit microbial growth and enzymatic spoilage.
- Pickling and Fermentation: Using acidic or anaerobic environments to preserve food and often enhance flavor.
Understanding how refrigeration complements these other methods can lead to more effective and versatile food preservation strategies.
The Future of Food Refrigeration: Innovation and Sustainability
The field of food refrigeration continues to evolve, driven by the need for greater energy efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced food safety. Innovations include:
- Smart Refrigerators: Equipped with sensors, connectivity, and AI to optimize storage, track food inventory, and even suggest recipes based on available ingredients.
- More Energy-Efficient Refrigeration Technologies: Research and development into alternative refrigerants and more efficient cooling cycles to reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Advanced Temperature and Humidity Control Systems: Precision control to create optimal environments for different types of food within the same appliance.
- Sustainable Refrigeration Practices: Focus on reducing food waste through better preservation techniques and promoting responsible consumption.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Proper Food Refrigeration
Food refrigeration is more than just keeping food cold; it’s a science, an art, and a fundamental aspect of ensuring food safety, preserving nutritional value, and minimizing waste. By understanding the principles of refrigeration, mastering proper storage techniques, and staying informed about advancements in cooling technology, you can significantly enhance the quality and longevity of your food. Embrace the power of effective food refrigeration and contribute to a healthier, safer, and more sustainable food system.