Is your refrigerator not performing at its best? Don’t rush to replace it! Often, the solution lies in identifying and replacing the faulty component. Our comprehensive guide delves deep into the intricate world of fridge appliance parts, providing you with the knowledge and understanding to diagnose issues, source the correct replacements, and potentially save significant time and money. We’ll explore everything from the most common culprits behind refrigerator malfunctions to preventative maintenance tips that can extend the life of your invaluable kitchen appliance.
Identifying Common Fridge Problems and the Corresponding Appliance Parts

A malfunctioning refrigerator can disrupt your entire household. Understanding the symptoms can often point you towards the specific fridge part that needs attention. Let’s explore some frequent issues and the components typically involved:

- No Cooling or Insufficient Cooling: This is a widespread concern and could stem from several refrigerator parts. Potential culprits include a faulty compressor, the heart of the cooling system; a malfunctioning condenser fan motor, responsible for dissipating heat; an issue with the evaporator fan motor, which circulates cold air within the fridge and freezer compartments; or a problem with the defrost system, such as a faulty defrost heater, defrost thermostat, or defrost timer/control board, leading to excessive frost buildup that hinders cooling. Refrigerant leaks, while less common for DIY fixes, can also cause this issue.
- Excessive Frost Buildup: As mentioned above, problems within the defrost system are the primary cause. The defrost heater melts away frost, the defrost thermostat monitors the temperature of the evaporator coils, and the defrost timer or electronic control board initiates the defrost cycle. A failure in any of these fridge components can lead to ice accumulation, reducing efficiency and potentially damaging other parts.
- Water Leaks: Leaks can originate from various sources. A cracked or improperly connected water line supplying the ice maker or water dispenser is a common cause. Issues with the water inlet valve, which controls the flow of water, or a clogged or damaged drain pan located beneath the evaporator coils can also lead to leaks. In refrigerators with automatic defrost, a blocked defrost drain can cause water to overflow and leak inside the fridge.
- No Ice Production: If your ice maker isn’t producing ice, the problem could lie with the ice maker assembly itself, the water inlet valve that supplies water to the ice maker, or a frozen water line. Sometimes, the issue is as simple as the bail arm being in the “off” position, but other times, a specific ice maker part needs replacement.
- Water Dispenser Not Working: Similar to ice maker issues, a faulty water inlet valve or a frozen or clogged water line can prevent water dispensing. Problems with the dispenser switch or the electronic control board could also be responsible.
- Noisy Operation: Unusual noises can indicate a problem with various refrigerator components. A failing condenser fan motor or evaporator fan motor can produce whirring or grinding sounds. A noisy compressor might signal a more serious issue. Loose or vibrating components can also contribute to unwanted noise.
- Light Not Working: While seemingly minor, a non-functional refrigerator light can be inconvenient. The issue could be a burnt-out light bulb (or LED), a faulty light socket, or a problem with the door switch that activates the light when the door is opened.
- Door Not Sealing Properly: A worn or damaged door gasket (also known as a door seal) allows warm air to enter the refrigerator, forcing it to work harder and potentially leading to food spoilage. Inspecting and replacing the door gasket is often a simple but effective fix.

Understanding the Essential Fridge Appliance Parts and Their Functions
To effectively troubleshoot and repair your refrigerator, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the key appliance parts and their roles in the cooling process and overall operation:
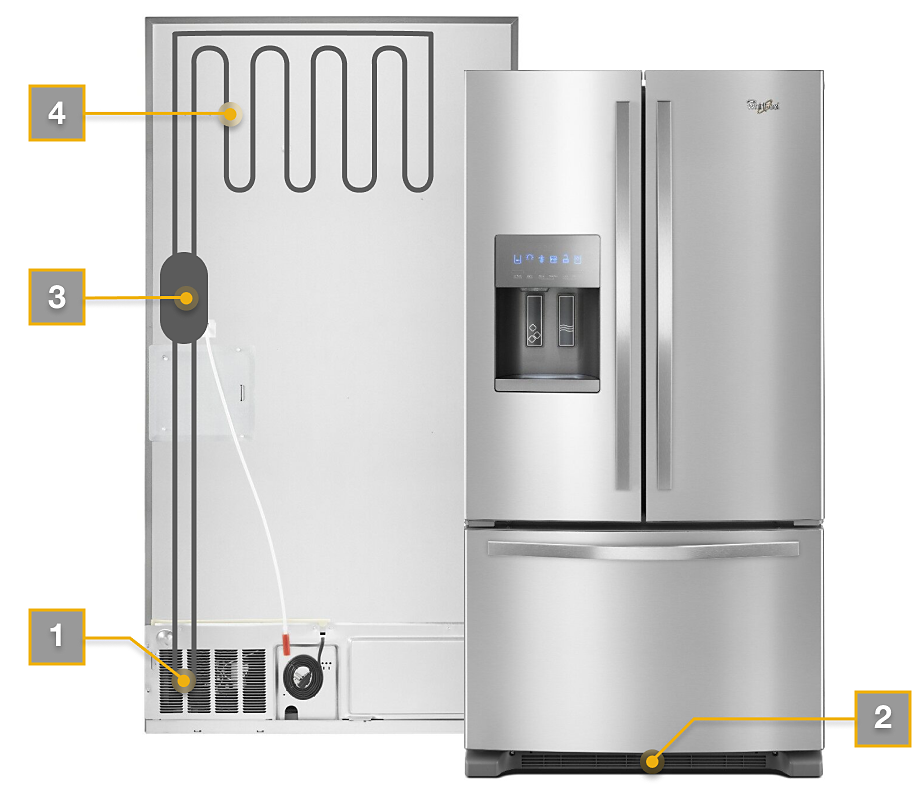
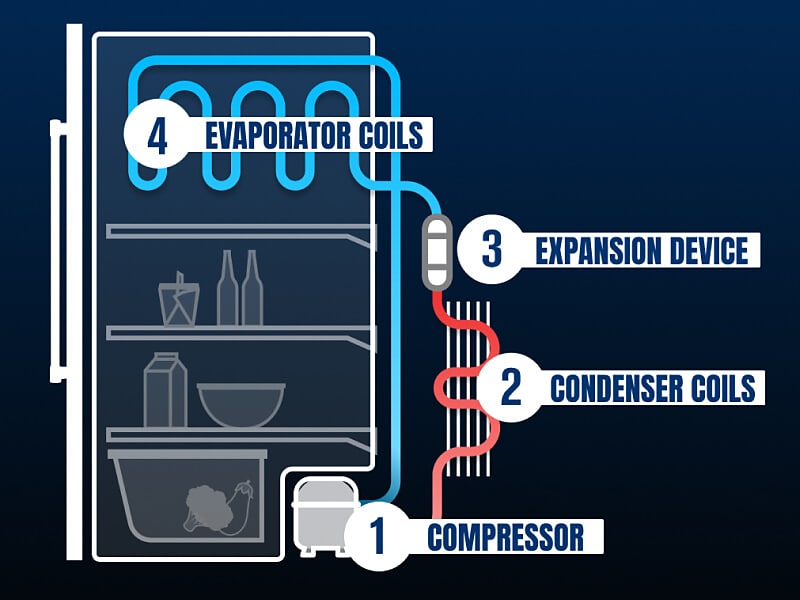
- Compressor: The heart of the refrigeration system, the compressor circulates refrigerant through the coils, compressing it and raising its temperature.
- Condenser Coils: Located on the exterior (usually at the back or underneath), the condenser coils dissipate the heat from the compressed refrigerant, turning it into a high-pressure liquid.
- Evaporator Coils: Located inside the freezer compartment, the evaporator coils absorb heat from the air inside the refrigerator as the liquid refrigerant evaporates, creating the cooling effect.
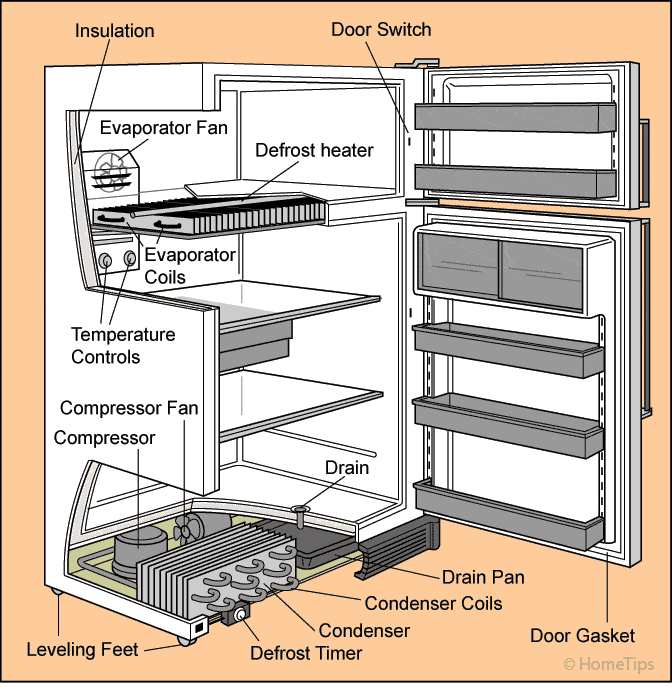
- Evaporator Fan Motor: This motor circulates the cold air produced by the evaporator coils throughout the refrigerator and freezer compartments, ensuring even cooling.
- Condenser Fan Motor: This fan helps to cool the condenser coils, facilitating the heat dissipation process.
- Defrost Heater: This electrical heating element melts away any frost that accumulates on the evaporator coils, ensuring efficient cooling.
- Defrost Thermostat (or Bi-metal): This temperature-sensitive switch monitors the temperature of the evaporator coils and signals the defrost timer or control board when the coils are cold enough to end the defrost cycle.
- Defrost Timer or Electronic Control Board: This component controls the defrost cycle, determining when the defrost heater should turn on and off. Modern refrigerators often use an electronic control board that manages various functions, including defrost.
- Water Inlet Valve: This electrically controlled valve regulates the flow of water to the ice maker and water dispenser.
- Ice Maker Assembly: This unit is responsible for producing ice, typically consisting of a mold, heating element, and ejector arm.
- Water Filter: Located either inside the refrigerator or externally, the water filter removes impurities from the water supply before it reaches the ice maker and water dispenser, ensuring clean and fresh-tasting water and ice.
- Door Gasket (Seal): This rubber or magnetic strip around the refrigerator and freezer doors creates an airtight seal, preventing warm air from entering and cold air from escaping.
- Thermostat: This component senses the temperature inside the refrigerator and controls the compressor and fans to maintain the desired temperature. In modern refrigerators, this function is often integrated into the electronic control board.
- Overload Protector and Relay: These electrical components protect the compressor from overheating and help start the motor.

Empowering You: Troubleshooting and DIY Repair of Fridge Appliance Parts
While some refrigerator repairs require professional expertise, many common issues can be addressed through careful troubleshooting and DIY replacement of fridge appliance parts. Before attempting any repairs, always remember to disconnect the refrigerator from the power source to ensure your safety.
- Diagnosis is Key: Carefully observe the symptoms your refrigerator is exhibiting. Is it not cooling at all? Is there excessive frost? Are there unusual noises? Refer to the “Common Fridge Problems” section above to narrow down potential causes.
- Consult Your Refrigerator’s Manual: Your owner’s manual often contains valuable troubleshooting tips and diagrams of refrigerator parts.
- Online Resources: Numerous online resources, including manufacturer websites, appliance parts retailers, and DIY forums, offer helpful guides and videos for diagnosing and repairing specific issues.
- Identifying the Correct Part: Once you’ve identified the likely culprit, you’ll need to find the correct replacement fridge part. Ensure you have your refrigerator’s model number, which is usually located on a sticker inside the refrigerator compartment. Use this model number to search for compatible appliance parts from reputable suppliers.
- Replacing the Part: Many refrigerator parts are relatively straightforward to replace with basic tools. However, some repairs, particularly those involving the sealed refrigeration system (e.g., compressor replacement, refrigerant leaks), require specialized equipment and should only be performed by qualified technicians.
- Safety First: Always prioritize safety. Disconnect the power, wear appropriate safety gear (e.g., gloves), and be cautious when handling electrical components.
Common DIY repairs often involve replacing the water filter, door gasket, light bulb, evaporator fan motor, or condenser fan motor. More complex repairs, such as replacing the defrost heater, defrost thermostat, or water inlet valve, may require more technical skill but can still be accomplished by a determined DIYer with the right guidance.
Proactive Care: Extending the Lifespan of Your Refrigerator Through Proper Maintenance
Regular maintenance can significantly extend the lifespan of your refrigerator and prevent costly repairs. Here are some essential tips:
- Clean the Condenser Coils: Dust and debris buildup on the condenser coils can hinder heat dissipation, making your refrigerator work harder and less efficiently. Clean the coils with a vacuum cleaner brush attachment every 6-12 months.
- Replace the Water Filter Regularly: If your refrigerator has a water filter, replace it according to the manufacturer’s recommendations (typically every 6 months) to ensure clean water and ice and prevent clogs.
- Clean the Door Gaskets: Regularly clean the door gaskets with a damp cloth to remove food debris and prevent them from becoming sticky or damaged, ensuring a proper seal.
- Don’t Overload the Refrigerator: Overpacking the refrigerator can restrict airflow, making it harder for the unit to maintain a consistent temperature.
- Check and Adjust Temperature Settings: Ensure your refrigerator and freezer are set to the optimal temperatures (typically 35-40°F for the refrigerator and 0°F for the freezer).
- Level the Refrigerator: An uneven refrigerator can put stress on the doors and seals. Adjust the leveling feet to ensure the unit is level.
- Promptly Address Minor Issues: Don’t ignore unusual noises or minor leaks. Addressing small problems early can prevent them from escalating into more significant and expensive repairs.
Sourcing Quality Fridge Appliance Parts: Ensuring Compatibility and Reliability
When it comes to replacing fridge appliance parts, quality and compatibility are paramount. Here are some tips for finding the right components:
- Know Your Model Number: As mentioned earlier, your refrigerator’s model number is crucial for finding compatible appliance parts.
- Reputable Suppliers: Purchase fridge parts from reputable appliance parts retailers or authorized distributors to ensure quality and reliability.
- OEM vs. Aftermarket Parts: Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) parts are made by the same manufacturer as your refrigerator and are guaranteed to fit and function correctly. Aftermarket parts may be more affordable but ensure they are from a trusted brand and specifically designed for your model.
- Read Reviews: If purchasing online, read reviews from other customers to gauge the quality and reliability of the fridge parts and the supplier.
- Check Warranty Information: Some replacement appliance parts come with a warranty. Be sure to understand the terms and conditions.
© [Your Company Name/Website Name] – Your Trusted Resource for Fridge Appliance Parts