In today’s world, where environmental consciousness and financial prudence go hand-in-hand, choosing the right appliances for your home has never been more critical. Among these, the refrigerator stands out as a constant energy consumer, operating 24/7. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the realm of energy-efficient refrigerators, illuminating how these modern marvels can revolutionize your energy consumption, drastically reduce your utility bills, and contribute to a healthier planet. Prepare to discover the innovative technologies, key features, and expert advice that will empower you to make an informed decision and invest in a refrigerator that truly aligns with your values and needs.
Why Choose an Energy-Efficient Refrigerator? Beyond the Savings
While the immediate benefit of lower electricity bills is undeniably attractive, the advantages of opting for an energy-efficient refrigerator extend far beyond mere monetary savings. By choosing a model with superior energy performance, you are actively participating in a larger movement towards sustainability and responsible resource management. Let’s explore the multifaceted benefits:
- Significant Reduction in Energy Consumption: Energy-efficient refrigerators are engineered with cutting-edge technologies that minimize the amount of electricity required for operation. This translates directly into lower kilowatt-hour usage on your monthly bills.
- Lower Utility Bills: Over the lifespan of a refrigerator, the cumulative savings from reduced energy consumption can be substantial, often exceeding the initial price difference compared to less efficient models.
- Environmental Responsibility: By consuming less energy, these refrigerators contribute to a smaller carbon footprint. This helps reduce the demand for fossil fuels and mitigates the impact of greenhouse gas emissions on our planet.
- Quieter Operation: Many energy-efficient refrigerators utilize advanced compressor technologies and improved insulation, resulting in significantly quieter operation compared to older or less efficient models. This creates a more peaceful and comfortable home environment.
- Potential for Government Incentives and Rebates: In many regions, governments and utility companies offer incentives, tax credits, or rebates for purchasing energy-efficient appliances, further reducing the overall cost of ownership.
- Extended Appliance Lifespan: Often built with higher-quality components and more robust engineering to achieve energy efficiency, these refrigerators can potentially have a longer lifespan, offering better long-term value.
- Enhanced Features and Innovation: The pursuit of energy efficiency often drives innovation. Energy-efficient refrigerators frequently come equipped with advanced features such as smart controls, improved temperature management, and better food preservation technologies.
Decoding the Efficiency: Key Technologies and Features
The remarkable energy savings offered by modern refrigerators are a result of sophisticated engineering and the integration of several key technologies and features. Understanding these elements will empower you to discern truly energy-efficient models from those that merely claim to be.
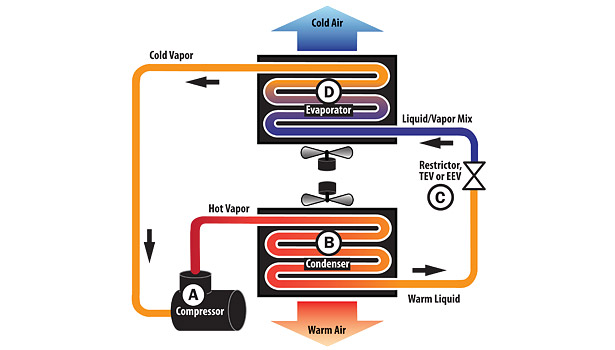
The Power of the Inverter Compressor
One of the most significant advancements in refrigerator technology is the inverter compressor. Unlike traditional compressors that operate at a fixed speed, cycling on and off at full power, inverter compressors can adjust their speed based on the cooling demand. This variable speed operation offers numerous advantages:
- Consistent Temperature: By maintaining a more consistent internal temperature, food stays fresher for longer, reducing spoilage.
- Reduced Energy Consumption: The compressor only uses the necessary amount of power to maintain the desired temperature, leading to significant energy savings compared to fixed-speed compressors.
- Quieter Operation: The gradual changes in compressor speed result in smoother and quieter operation.
- Longer Lifespan: The reduced stress on the compressor from constant on-off cycling can contribute to a longer lifespan.


Superior Insulation: Keeping the Cold In
Effective insulation is crucial for minimizing heat transfer into the refrigerator, thereby reducing the workload on the cooling system. Modern energy-efficient refrigerators utilize advanced insulation materials and techniques, such as:
- High-Density Foam Insulation: Thicker and more efficient foam insulation minimizes heat leakage.
- Vacuum Insulation Panels (VIPs): These panels offer exceptional insulation performance in a thinner profile, allowing for more internal storage space without increasing external dimensions.
Smart Controls and Sensors: Optimizing Performance
Intelligent sensors and control systems play a vital role in optimizing energy efficiency. These features include:
- Temperature Sensors: Precisely monitor internal and external temperatures to adjust cooling output as needed.
- Door Open Sensors: Detect when the doors are open and can temporarily adjust cooling to compensate for temperature fluctuations.
- Adaptive Defrost Systems: Only initiate defrost cycles when necessary, rather than on a fixed schedule, saving energy.
- Vacation Mode: Allows you to set the refrigerator to a higher energy-saving temperature when you are away for an extended period.


Natural Refrigerants: An Eco-Conscious Choice
The type of refrigerant used in a refrigerator also has a significant impact on its environmental footprint. Energy-efficient refrigerators are increasingly utilizing natural refrigerants like R600a (isobutane) and R290 (propane), which have a much lower global warming potential compared to traditional synthetic refrigerants.
Optimized Airflow and Cooling Systems
Efficient airflow design ensures even temperature distribution throughout the refrigerator compartments, preventing hot spots and allowing the cooling system to operate more effectively with less energy.
LED Lighting: Bright and Efficient
Energy-efficient refrigerators almost universally utilize LED lighting. LEDs consume significantly less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs and also generate less heat, further reducing the cooling load on the refrigerator.
Navigating the Choices: Types of Energy-Efficient Refrigerators
The market offers a diverse range of refrigerator styles, each with its own energy efficiency characteristics. Understanding these different types will help you narrow down your options based on your specific needs and preferences.
- Top-Freezer Refrigerators: Generally the most energy-efficient type due to their simpler design and the natural tendency of cold air to sink, reducing energy loss between compartments.
- Bottom-Freezer Refrigerators: Offer good energy efficiency, although typically slightly less efficient than top-freezer models. The more frequently accessed refrigerator compartment is at a convenient height.
- Side-by-Side Refrigerators: Tend to be less energy-efficient due to the larger surface area exposed to the ambient air and the vertical division between the freezer and refrigerator compartments. However, newer models are incorporating more energy-saving technologies.
- French Door Refrigerators: Combine the convenience of a bottom freezer with wide refrigerator compartments and two doors. Energy efficiency varies depending on the specific model and features.
- Compact and Mini Refrigerators: While often used in smaller spaces, their energy efficiency can vary widely. Look for Energy Star certified models for the best performance.
Expert Advice: How to Choose the Right Energy-Efficient Refrigerator
Selecting the ideal energy-efficient refrigerator requires careful consideration of several factors. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you make the right choice:
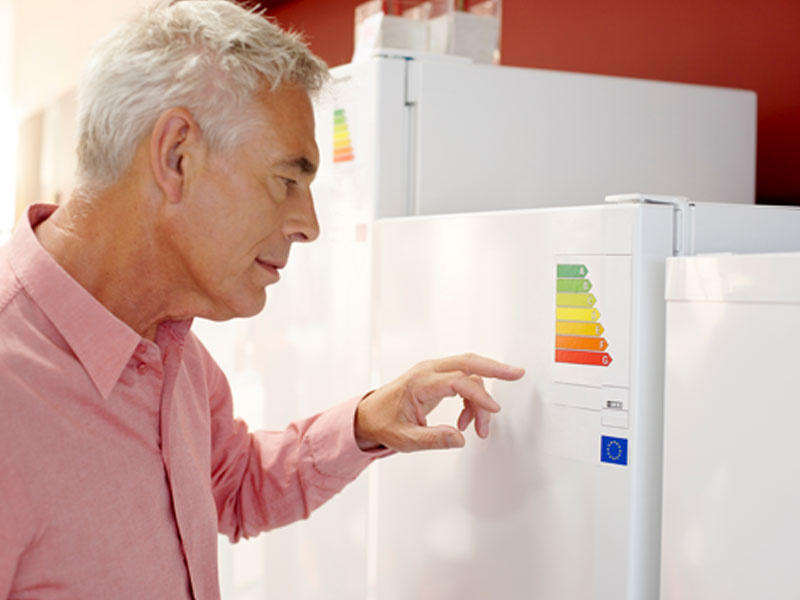
- Look for the Energy Star Label: This is the most reliable indicator of energy efficiency. Energy Star certified refrigerators meet strict guidelines set by environmental agencies, ensuring significant energy savings.
- Consider the Climate Zone: Refrigerators are tested and rated for different climate zones. Choose a model that is appropriate for the climate where you live for optimal energy performance.
- Assess Your Storage Needs: Choose a size and configuration that meets your household’s needs without being unnecessarily large. A larger refrigerator consumes more energy, even if it’s energy-efficient.
- Evaluate Features vs. Efficiency: While desirable features like ice makers and water dispensers can add convenience, they can also increase energy consumption. Consider how often you will actually use these features.
- Check the Energy Consumption Rating: The Energy Star label provides an estimated annual energy consumption in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Compare this rating across different models to see which one is the most efficient.
- Consider the Compressor Type: Opt for models with inverter compressors for superior energy efficiency and quieter operation.
- Examine the Insulation: Look for mentions of high-density foam or vacuum insulation panels for better thermal performance.
- Read Reviews and Compare Models: Research different brands and models, and read customer reviews to get insights into real-world performance and reliability.
- Factor in the Total Cost of Ownership: Consider not only the initial purchase price but also the estimated annual energy cost over the lifespan of the refrigerator. An energy-efficient model might have a slightly higher upfront cost but can save you significantly more money in the long run.
- Explore Smart Features: Some energy-efficient refrigerators offer smart features that can further optimize energy usage, such as remote monitoring and control.

Maximizing Efficiency: Tips for Using Your Energy-Efficient Refrigerator
Even the most energy-efficient refrigerator can consume more energy if not used properly. Here are some practical tips to maximize its efficiency:
- Maintain the Recommended Temperature Settings: The ideal temperature for the refrigerator compartment is between 35-40°F (2-4°C), and for the freezer compartment, it’s around 0°F (-18°C). Lower temperatures consume more energy.
- Avoid Overpacking: While a full refrigerator stays colder more efficiently (as the food helps retain the cold), overpacking can restrict airflow, making the refrigerator work harder.
- Don’t Place Hot Food Inside: Allow hot food to cool down to room temperature before placing it in the refrigerator to avoid increasing the internal temperature and making the compressor work harder.
- Minimize Door Openings and Duration: Every time you open the door, cold air escapes, and the refrigerator has to use energy to cool back down. Plan what you need before opening the door and close it quickly.
- Ensure Proper Door Seals: Check the door seals regularly to make sure they are clean and create a tight seal. A faulty seal allows cold air to escape, increasing energy consumption. You can test the seal by closing the door on a piece of paper; if you can easily pull it out, the seal may need attention.
- Keep the Condenser Coils Clean: The condenser coils, usually located at the back or bottom of the refrigerator, dissipate heat. Dust and debris buildup on these coils can reduce their efficiency, forcing the compressor to work harder. Clean them regularly with a vacuum cleaner brush attachment.
- Defrost Regularly (for Manual Defrost Models): Frost buildup in the freezer acts as an insulator, reducing efficiency. If you have a manual defrost model, defrost it regularly to maintain optimal performance. Frost-free models handle this automatically.
- Position Your Refrigerator Wisely: Avoid placing your refrigerator near heat sources such as ovens, dishwashers, or direct sunlight. These external heat sources will make the refrigerator work harder to stay cool. Ensure adequate ventilation around the refrigerator to allow for proper heat dissipation.
© 2025 All Rights Reserved. Your Resource for Energy-Efficient Home Appliances.