Understanding the Critical Role of Retail Freezers in Your Business Ecosystem
In the dynamic landscape of modern retail, particularly within the food and beverage sector, the retail freezer stands as a cornerstone of operational efficiency, product integrity, and ultimately, profitability. More than just a cold storage unit, the right retail freezer is a strategic asset that directly impacts customer satisfaction, inventory management, and energy consumption. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the multifaceted world of retail freezers, providing you with the knowledge and insights necessary to make informed decisions that will elevate your business to new heights.
From bustling supermarkets and convenience stores to specialized gourmet food shops and catering services, the need for reliable and efficient frozen storage is paramount. The selection of an inappropriate or underperforming retail freezer can lead to a cascade of negative consequences, including product spoilage, increased energy costs, compromised food safety, and a diminished customer experience. Conversely, a well-chosen and meticulously maintained retail freezer can streamline operations, preserve the quality and appeal of your frozen goods, attract customers with enticing displays, and contribute significantly to your bottom line.
Navigating the Diverse Landscape of Retail Freezer Types: Finding the Perfect Fit for Your Needs
The market offers a wide array of retail freezer types, each designed to cater to specific needs and applications. Understanding these distinctions is crucial in selecting the optimal solution for your business. Let’s explore some of the most prevalent categories:
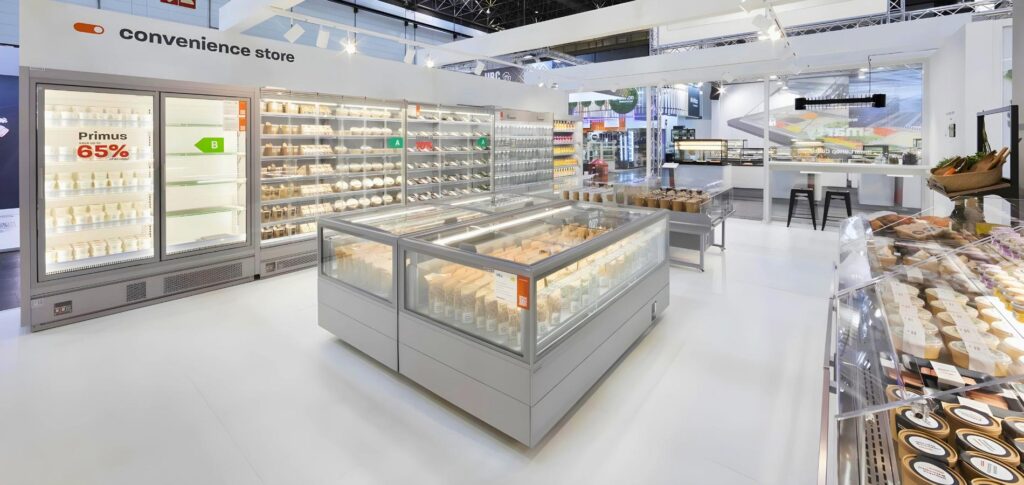
- Display Freezers: These are designed to showcase frozen products to customers, encouraging impulse purchases and maximizing visual appeal. They come in various formats, including:
- Glass Door Freezers: Offering excellent visibility and energy efficiency compared to open-top models, glass door freezers are ideal for supermarkets and convenience stores displaying a wide range of frozen foods. They help maintain consistent temperatures and reduce energy loss.
- Chest Freezers with Glass Lids: Providing a balance between visibility and storage capacity, these are often used for showcasing promotional items or high-volume products.
- Open-Top Island Freezers: Strategically placed in high-traffic areas, these freezers encourage impulse buys. However, they tend to be less energy-efficient than closed models.
- Serve-Over Freezers: Commonly found in delis and butcher shops, these freezers allow staff to serve frozen items directly to customers.
When selecting the appropriate type of retail freezer, consider factors such as your available floor space, the volume and type of products you need to store and display, your budget, and your energy efficiency goals.
Key Features and Considerations When Investing in a Retail Freezer
Beyond the basic type, several crucial features and considerations will significantly impact the performance, efficiency, and longevity of your retail freezer investment:
- Temperature Control and Consistency: The ability to maintain a stable and accurate temperature is paramount for preserving the quality and safety of frozen goods. Look for freezers with reliable thermostats and efficient cooling systems.
- Energy Efficiency: Retail freezers operate continuously, making energy consumption a significant operational cost. Opting for energy-efficient models with features like high-quality insulation, efficient compressors, and LED lighting can lead to substantial savings over time. Look for Energy Star certified models.
- Storage Capacity and Layout: Choose a freezer with sufficient capacity to meet your current and anticipated needs. Consider the internal layout and shelving options to optimize organization and accessibility.
- Durability and Build Quality: A retail freezer is a long-term investment. Select models constructed from high-quality materials that can withstand the rigors of daily commercial use.
- Maintenance Requirements: Consider the ease of cleaning and maintenance. Features like automatic defrost cycles can significantly reduce manual effort.
- Refrigerant Type: Be mindful of the type of refrigerant used, as some are more environmentally friendly than others. Regulations regarding refrigerants are constantly evolving.
- Noise Levels: In customer-facing areas, the noise level of the freezer can impact the shopping experience. Opt for quieter models when appropriate.
- Security Features: For storage freezers, consider features like locking mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access.
- Aesthetics and Design: For display freezers, the visual appeal can influence customer perception. Choose models that complement your store’s overall aesthetic.
Carefully evaluating these features will ensure that you select a retail freezer that not only meets your immediate needs but also contributes to the long-term success of your business.
Optimizing Performance and Longevity: Essential Retail Freezer Maintenance Practices
Investing in a high-quality retail freezer is only the first step. Consistent and proactive maintenance is crucial to ensure optimal performance, extend the lifespan of your equipment, and prevent costly breakdowns. Key maintenance practices include:
- Regular Cleaning: Clean the interior and exterior of the freezer regularly to remove dust, debris, and spills. This helps maintain hygiene and improve efficiency.
- Checking and Maintaining Door Seals: Damaged or worn door seals can lead to significant energy loss and temperature fluctuations. Inspect seals regularly and replace them when necessary.
- Cleaning Condenser Coils: Dirty condenser coils reduce the freezer’s ability to dissipate heat, leading to increased energy consumption and potential compressor failure. Clean the coils at least every three to six months.
- Monitoring Temperature Regularly: Use a reliable thermometer to ensure that the freezer is maintaining the correct temperature range. Adjust settings as needed.
- Implementing a Defrost Schedule: For manual defrost models, establish a regular defrosting schedule to prevent excessive ice buildup, which reduces efficiency and storage space.
- Professional Servicing: Schedule regular professional maintenance checks to identify and address potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
- Proper Loading and Organization: Avoid overpacking the freezer, which can impede airflow and reduce cooling efficiency. Organize items in a way that allows for easy access and proper circulation.

By adhering to these maintenance best practices, you can maximize the efficiency and lifespan of your retail freezer, minimizing downtime and ensuring the consistent quality of your frozen products.
Strategic Placement and Merchandising: Maximizing Sales with Your Retail Freezer
The strategic placement and effective merchandising of your retail freezers can significantly impact sales and customer engagement. Consider the following strategies:
- High-Traffic Areas: Position impulse-buy items in high-traffic areas to capture customer attention.
- End-Cap Displays: Utilize end-cap freezers to showcase promotional items or seasonal products.
- Complementary Product Placement: Place freezers near related items to encourage cross-selling (e.g., ice cream near cones and toppings).
- Attractive Signage and Lighting: Use clear and appealing signage and ensure adequate lighting to highlight your frozen products.
- Organized and Appealing Displays: Keep freezers well-organized and visually appealing to make it easy for customers to find what they are looking for.
- Regularly Rotate Stock: Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) system to ensure product freshness and minimize waste.
- Consider Eye-Level Placement: Position high-margin or popular items at eye level to maximize visibility.
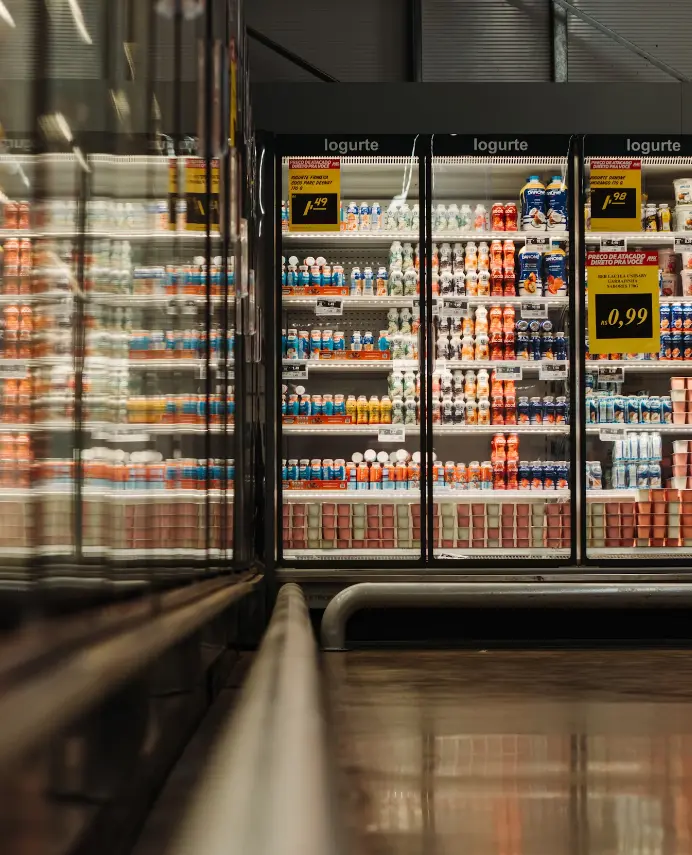

By thoughtfully positioning and merchandising your retail freezers, you can create a more engaging shopping experience and drive increased sales of your frozen goods.
The Future of Retail Freezers: Innovations and Trends to Watch
The retail freezer industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies and trends emerging to enhance efficiency, sustainability, and customer experience. Some key areas to watch include:
- Smart Freezer Technology: Incorporating sensors, IoT connectivity, and data analytics to optimize temperature control, monitor inventory levels, and predict maintenance needs.
- Sustainable Refrigerants: A growing focus on environmentally friendly refrigerants with lower global warming potential.
- Improved Energy Efficiency: Continued advancements in insulation materials, compressor technology, and lighting systems to reduce energy consumption.
- Enhanced Display Technologies: Innovations in glass door design, lighting, and digital signage to create more visually appealing and informative displays.
- Customizable and Modular Designs: Freezers that can be easily adapted to changing business needs and store layouts.

Staying informed about these advancements will allow you to make future-proof investment decisions and leverage the latest technologies to optimize your retail freezer operations.
© 2025 All Rights Reserved. This comprehensive guide provides valuable insights into retail freezers.

















.webp)




















