Understanding the Critical Role of Kerosene Vaccine Refrigerators
In remote and resource-limited areas, maintaining the integrity of vaccines is paramount. Kerosene vaccine refrigerators play a vital role in the cold chain, ensuring vaccines remain at optimal temperatures. Unlike electric refrigerators, these units rely on kerosene, making them indispensable in regions with unreliable or non-existent power grids. The vaccine log is the cornerstone of this process, providing a documented history of temperature fluctuations and maintenance.
The Importance of a Detailed Vaccine Log
A comprehensive vaccine log serves several critical purposes:
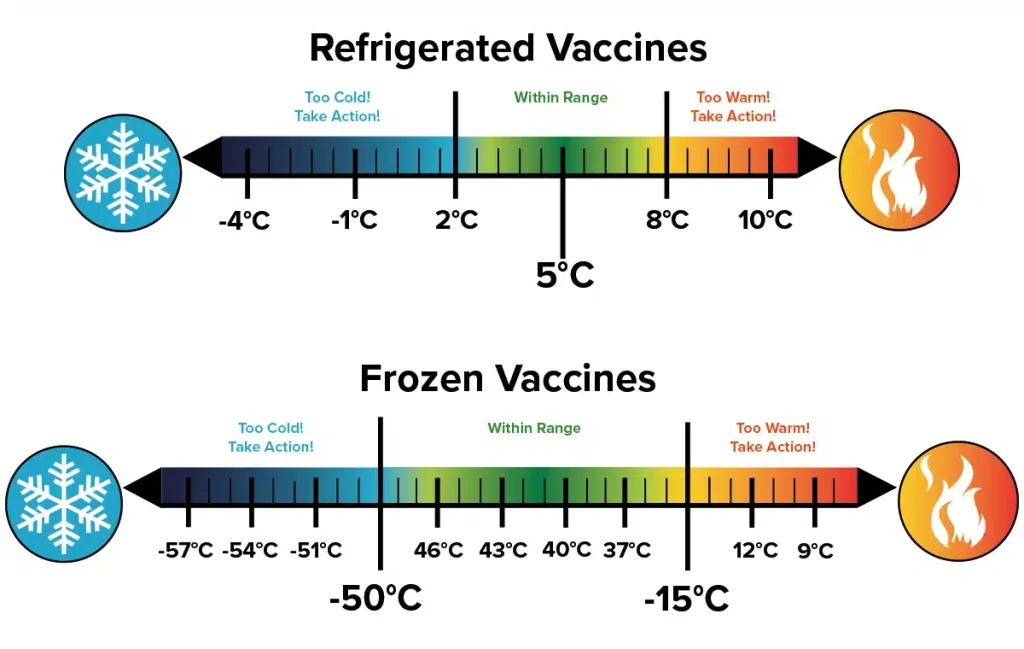
- Temperature Monitoring: It records the internal temperature of the refrigerator at regular intervals, typically twice daily. This ensures vaccines are consistently stored within the recommended temperature range (usually +2°C to +8°C).
- Maintenance Tracking: The log should document all maintenance activities, including kerosene refills, burner cleaning, and any repairs. This helps identify potential issues and ensure the refrigerator is functioning optimally.
- Accountability and Compliance: A well-maintained log provides evidence of proper vaccine storage, which is crucial for audits and regulatory compliance. It also helps healthcare workers stay accountable for maintaining the cold chain.
- Problem Identification: By analyzing the log, healthcare workers can identify patterns of temperature fluctuations or maintenance issues, allowing for timely intervention and preventing vaccine spoilage.
Essential Components of a Kerosene Vaccine Refrigerator Log

A robust kerosene vaccine refrigerator log should include the following information:
- Date and Time: Each entry must include the date and time of the temperature reading.
- Temperature Readings: Record the maximum and minimum temperatures since the last reading.
- User Initials: The healthcare worker who took the reading should initial each entry.
- Maintenance Activities: Detail any maintenance performed, including kerosene refills, burner cleaning, and repairs.
- Observations: Note any unusual observations, such as changes in flame color, frost buildup, or unusual noises.
- Action Taken: If any issues are identified, document the actions taken to address them.
Best Practices for Maintaining a Kerosene Vaccine Refrigerator and Log
To ensure the efficacy of your kerosene vaccine refrigerator, follow these best practices:
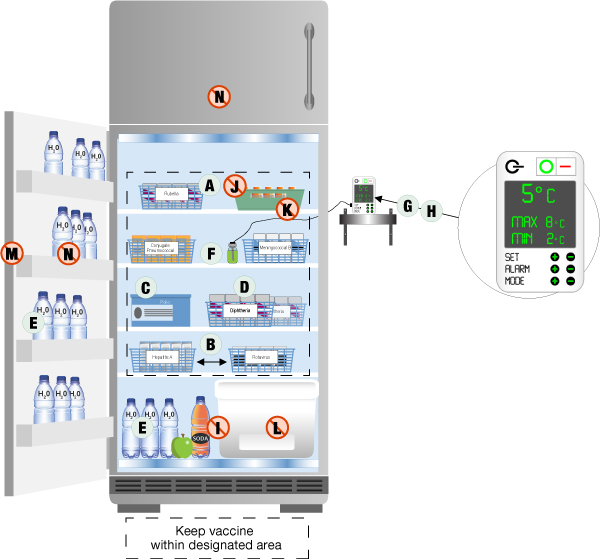
- Regular Temperature Checks: Monitor the temperature at least twice daily, preferably morning and evening.
- Proper Kerosene Handling: Use clean, high-quality kerosene and store it safely away from the refrigerator.
- Burner Maintenance: Clean the burner regularly to ensure efficient combustion and prevent soot buildup.
- Door Seals: Check the door seals regularly for leaks and replace them as needed.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation around the refrigerator to prevent overheating.
- Training: Provide comprehensive training to healthcare workers on proper refrigerator operation and log maintenance.
- Emergency Procedures: Develop and implement emergency procedures for power outages or refrigerator malfunctions.
- Log Review: Review the temperature log regularly to identify trends and address potential issues proactively.
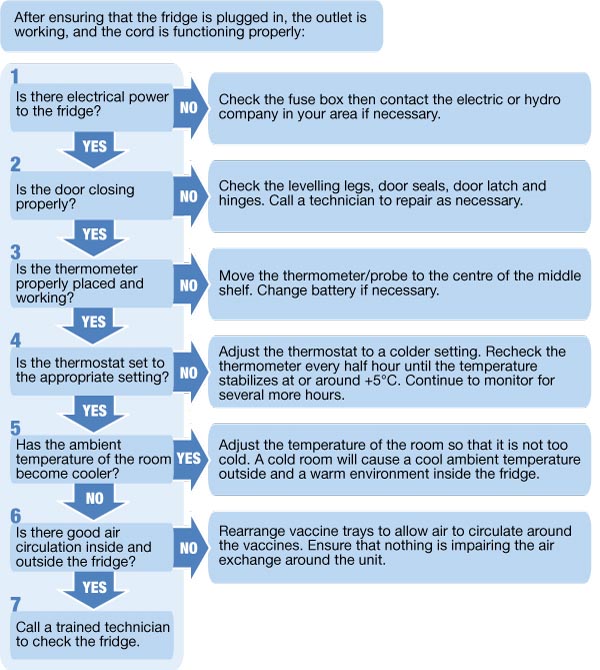
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with careful maintenance, issues can arise. Understanding common problems and their solutions is crucial:
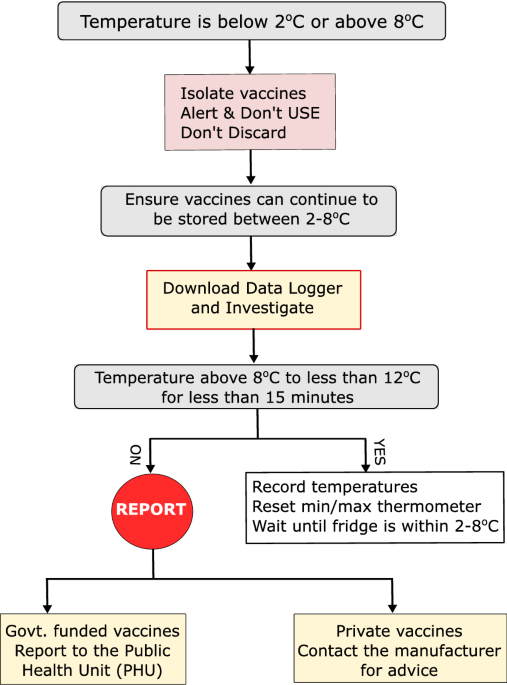
- Temperature Fluctuations: If the temperature fluctuates outside the recommended range, check the burner, door seals, and ventilation.
- Flame Issues: A yellow or smoky flame indicates incomplete combustion. Clean the burner and check the kerosene quality.
- Frost Buildup: Excessive frost buildup can affect temperature regulation. Defrost the refrigerator regularly and ensure proper door seals.
- Noisy Operation: Unusual noises may indicate a mechanical issue. Consult the manufacturer’s manual or a qualified technician.
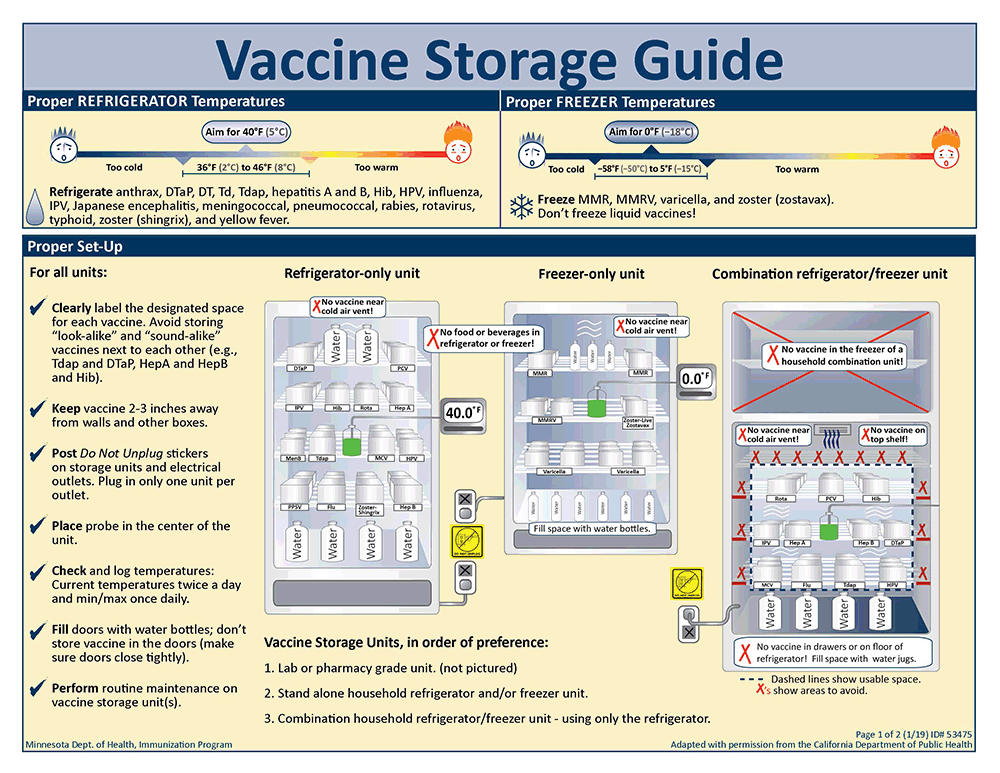
The Importance of the Cold Chain
The cold chain is a system of transporting and storing vaccines within a recommended temperature range. Maintaining this chain is vital to preserving vaccine potency and preventing wastage. Kerosene vaccine refrigerators and meticulous vaccine log keeping are essential components of a robust cold chain in remote settings.
Digital Solutions and the Future of Vaccine Logs
While traditional paper logs are effective, digital solutions are emerging to streamline the process. Electronic temperature monitors and digital logs offer real-time data, automated alerts, and remote access, enhancing efficiency and accuracy. However, in areas reliant on kerosene refrigerators, paper logs remain the most reliable method. As technology advances, a hybrid approach, combining digital monitoring with robust paper logs, may offer the best of both worlds.
Conclusion
The kerosene vaccine refrigerator log is a critical tool for ensuring the safe storage and efficacy of vaccines in remote areas. By maintaining a detailed log, healthcare workers can monitor temperature fluctuations, track maintenance activities, and ensure accountability. Proper log keeping, coupled with regular maintenance, is essential for preserving the integrity of the cold chain and protecting vulnerable populations. By adhering to best practices and staying vigilant, we can safeguard the potency of life-saving vaccines, even in the most challenging environments.