In the intricate and critical landscape of modern healthcare, research, and diagnostics, the medical freezer stands as an unsung hero, silently safeguarding the integrity and viability of invaluable biological samples, pharmaceuticals, and reagents. Far from being a mere appliance, a high-quality medical freezer is a sophisticated piece of equipment engineered with precision and reliability at its core. Its ability to maintain rigorously controlled low temperatures is paramount, directly impacting the accuracy of diagnostic tests, the efficacy of life-saving medications, and the validity of groundbreaking scientific discoveries. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the multifaceted world of medical freezers, exploring their diverse types, crucial features, stringent regulatory requirements, essential maintenance protocols, and the key considerations for selecting the optimal unit to meet specific operational demands. Understanding the nuances of medical freezer technology is not just a matter of operational efficiency; it is fundamentally linked to patient safety, research integrity, and the advancement of medical science itself.
Unveiling the Spectrum: Diverse Types of Medical Freezers for Varied Applications
The term “medical freezer” encompasses a broad range of specialized refrigeration units, each designed to cater to specific temperature requirements and storage needs within the medical and scientific communities. Recognizing these distinctions is crucial for ensuring the appropriate preservation of sensitive materials. Here’s an exploration of the primary types of medical freezers:
- Standard Medical Freezers: Operating typically within a temperature range of -10°C to -30°C, these freezers are commonly used for storing pharmaceuticals, vaccines (depending on specific requirements), general laboratory reagents, and certain biological samples that do not necessitate ultra-low temperatures. They often feature manual or auto-defrost cycles and offer a reliable solution for everyday cold storage needs.
- Laboratory Freezers: Often overlapping with standard medical freezers but potentially offering more advanced features like digital temperature control, enhanced security measures (such as key locks or electronic access), and more robust construction, laboratory freezers are designed for the demanding environment of research and clinical laboratories. They may come in various configurations, including upright, chest, and under-counter models, to optimize space utilization.
- Pharmaceutical Freezers: Given the stringent temperature control requirements for many medications and vaccines, pharmaceutical freezers are engineered for exceptional temperature stability and uniformity. They often feature sophisticated monitoring systems, alarm functionalities to alert users of temperature deviations, and robust security to protect valuable and often temperature-sensitive inventory. Compliance with regulatory standards is a paramount consideration for these units.
- Blood Bank Freezers: Specifically designed for the safe and regulated storage of blood components such as plasma, blood bank freezers adhere to strict temperature guidelines (typically around -30°C) to maintain the viability and efficacy of these critical life-saving products. They often incorporate features like specialized racking systems for organized storage and retrieval, as well as comprehensive temperature monitoring and recording capabilities to ensure compliance with blood banking regulations.
- Ultra-Low Temperature (ULT) Freezers: These high-performance freezers are capable of achieving and maintaining extremely low temperatures, typically ranging from -50°C to -86°C. ULT freezers are indispensable for the long-term preservation of highly sensitive biological samples, including DNA, RNA, proteins, and cell lines. They employ specialized refrigeration systems and insulation to achieve these extreme temperatures and are critical for research institutions, biobanks, and advanced diagnostic laboratories.
- Cryogenic Freezers: Operating at even lower temperatures, often utilizing liquid nitrogen or mechanical cryogenic systems, cryogenic freezers are employed for the long-term storage of biological materials at temperatures below -150°C. These systems are essential for preserving cells and tissues for extended periods, often for research or therapeutic applications.
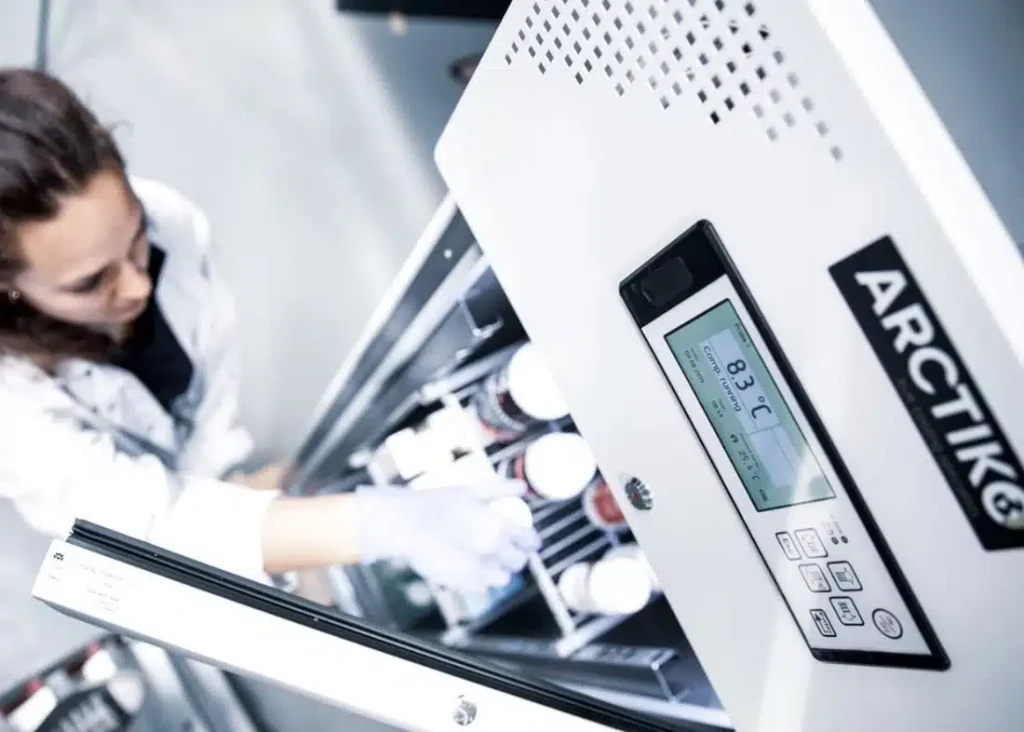


The selection of the appropriate medical freezer type hinges on a thorough understanding of the specific temperature requirements of the materials being stored, the volume of storage needed, space constraints, budgetary considerations, and relevant regulatory compliance obligations.
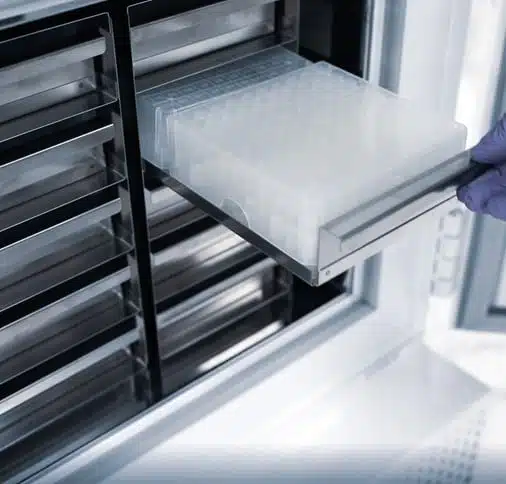

Key Features and Technological Advancements in Modern Medical Freezers

Modern medical freezers are equipped with a range of features designed to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and user convenience. These advancements contribute significantly to maintaining sample integrity and operational efficiency:
- Precise Digital Temperature Control: Advanced microprocessors and digital displays allow for highly accurate temperature setting and monitoring, often with temperature uniformity throughout the chamber.
- Sophisticated Monitoring and Alarm Systems: Integrated temperature sensors and alarm systems provide real-time monitoring and alert users to any temperature deviations that could compromise the stored materials. These systems may include audible and visual alarms, as well as remote notification capabilities.
- Data Logging and Reporting: Many high-end medical freezers feature built-in data loggers that record temperature history, providing an audit trail for compliance and quality control purposes. Data can often be downloaded and analyzed for comprehensive record-keeping.
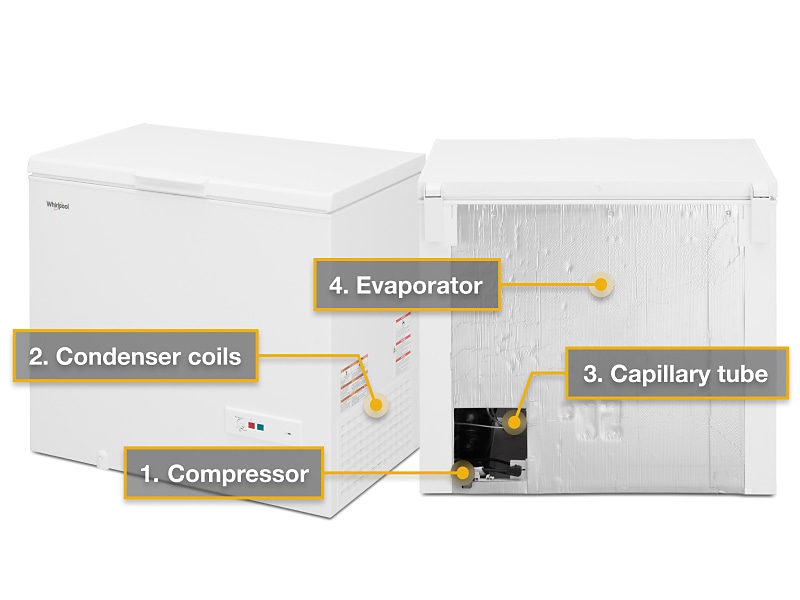
- Efficient Insulation and Refrigeration Systems: High-quality insulation materials and energy-efficient refrigeration systems are crucial for maintaining stable temperatures while minimizing energy consumption. This is particularly important for ULT freezers, which operate continuously at very low temperatures.
- Security Features: To protect valuable and sensitive contents, medical freezers often include security features such as key locks, electronic access control, and alarm systems that trigger upon unauthorized entry.
- Ergonomic Design and User-Friendly Interface: Features like adjustable shelving, easy-to-read displays, and intuitive controls enhance user convenience and facilitate efficient sample management.
- Defrost Systems: Depending on the type of freezer and its application, different defrost systems (manual, auto-defrost, or frost-free) are employed to prevent ice buildup and maintain optimal performance.
- Remote Monitoring Capabilities: Increasingly, medical freezers are equipped with connectivity features that allow for remote monitoring of temperature and alarm status, providing an added layer of security and convenience.
The integration of these features reflects the critical nature of the materials stored within medical freezers and the need for unwavering reliability and precise environmental control.
Navigating the Regulatory Landscape: Compliance and Standards for Medical Freezers
The operation and use of medical freezers are often subject to stringent regulatory guidelines and industry standards to ensure the safety, efficacy, and integrity of stored materials. These regulations can vary depending on the specific application (e.g., pharmaceutical storage, blood banking, research) and geographical location. Key considerations include:
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP): For pharmaceutical storage, compliance with GMP guidelines is essential, dictating requirements for equipment design, validation, and monitoring.
- Blood Banking Regulations: Blood banks must adhere to specific regulations governing the storage and handling of blood components, including strict temperature control and monitoring protocols.
- Laboratory Accreditation Standards: Laboratories may need to comply with accreditation standards that include requirements for the proper storage of samples and reagents.
- Temperature Mapping and Validation: Regular temperature mapping studies are often required to ensure temperature uniformity within the freezer chamber, and validation processes confirm that the equipment operates as intended.
- Record-Keeping and Audit Trails: Maintaining accurate temperature logs and alarm records is crucial for demonstrating compliance and ensuring accountability.
Understanding and adhering to these regulatory requirements is paramount for organizations utilizing medical freezers to avoid penalties, ensure the quality of their products or services, and ultimately protect patient safety and research integrity.
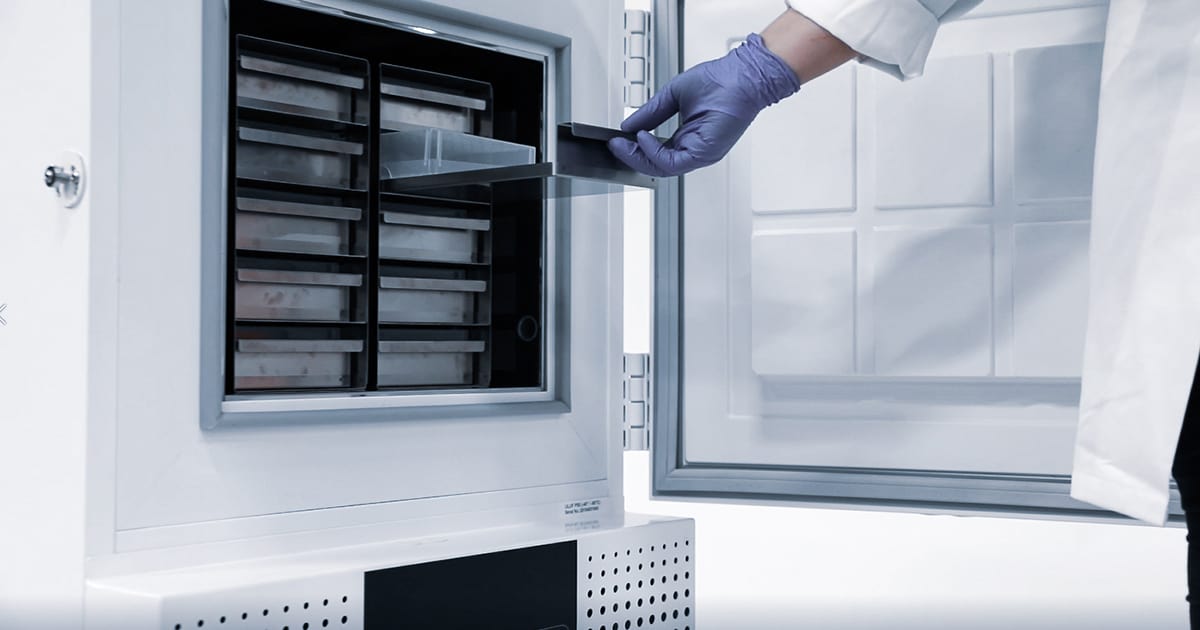
The Lifeline of Longevity: Essential Maintenance for Medical Freezers
To ensure the continued reliable performance and longevity of a medical freezer, regular and diligent maintenance is essential. Neglecting maintenance can lead to temperature fluctuations, equipment failures, and the potential loss of valuable stored materials. Key maintenance practices include:
- Regular Cleaning: Keeping the interior and exterior of the freezer clean helps to maintain hygiene and prevent dust buildup, which can affect performance.
- Defrosting (if applicable): Manual defrost freezers require periodic defrosting to remove ice buildup, which can reduce efficiency and storage capacity.
- Checking and Cleaning Door Seals: Damaged or dirty door seals can compromise temperature control. Regularly inspect and clean seals to ensure a tight closure.
- Monitoring Temperature and Alarms: Regularly verify the accuracy of the temperature display and ensure that alarm systems are functioning correctly.
- Inspecting Ventilation: Ensure that ventilation around the freezer is adequate to allow for proper heat dissipation.
- Preventative Maintenance: Schedule regular preventative maintenance checks by qualified technicians to identify and address potential issues before they lead to failures. This may include inspecting the refrigeration system, electrical components, and control systems.
- Calibration: Periodic calibration of temperature sensors ensures accurate temperature readings.

Implementing a proactive maintenance schedule is a crucial investment in the long-term reliability and cost-effectiveness of your medical freezer.
Making the Right Choice: Key Considerations When Selecting a Medical Freezer
Selecting the appropriate medical freezer for your specific needs requires careful consideration of several critical factors:
- Temperature Requirements: The most crucial factor is the specific temperature range required for the materials you will be storing. Ensure the freezer you choose can consistently maintain the necessary temperature.
- Storage Capacity: Determine the volume of storage needed, both currently and for future growth. Consider the internal organization and shelving options to maximize space utilization.
- Space Availability: Assess the physical space available for the freezer and choose a unit with appropriate dimensions and configuration (upright, chest, under-counter).
- Budget: Consider both the initial purchase cost and the ongoing operational costs, including energy consumption and maintenance.
- Reliability and Durability: Opt for reputable manufacturers known for producing high-quality and reliable equipment. Consider the expected lifespan and warranty offered.
- Security Features: If storing valuable or sensitive materials, prioritize freezers with appropriate security features.
- Energy Efficiency: Choose energy-efficient models to minimize operating costs and environmental impact.
- Compliance Requirements: Ensure the freezer meets any relevant regulatory standards or accreditation requirements for your specific application.
- User-Friendliness: Consider the ease of use, maintenance requirements, and the availability of technical support.

By carefully evaluating these factors, you can make an informed decision and select a medical freezer that effectively meets your needs, ensures the integrity of your stored materials, and provides years of reliable service.
The information provided in this guide is intended for general informational purposes only and should not be considered as professional advice. Always consult with qualified professionals for specific guidance related to your medical freezer needs and regulatory requirements.