
Understanding the relationship between pressure and temperature in R134a refrigerant is essential for diagnosing, maintaining, and repairing air conditioning and refrigeration systems. This guide will provide you with a comprehensive overview of the R134a pressure temperature chart and how to use it effectively.
What is R134a?
R134a is a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) refrigerant widely used in automotive air conditioning, residential and commercial refrigeration, and chillers. It replaced R12 due to its lower ozone depletion potential. However, it’s important to note that R134a has a significant global warming potential, and newer refrigerants with lower environmental impact are being developed.
The Importance of the Pressure Temperature Chart
The pressure temperature chart, also known as a saturation table, provides a direct correlation between the pressure and temperature of a refrigerant at saturation. This means it shows the boiling point of R134a at different pressures. Using this chart allows technicians to:
- Diagnose system problems: By comparing measured pressures and temperatures with the chart, you can identify issues like refrigerant leaks, restrictions, or overcharging.
- Determine superheat and subcooling: These measurements are crucial for optimizing system performance and ensuring proper refrigerant charge.
- Verify system operation: The chart helps confirm that the system is operating within its design parameters.
Understanding the Chart
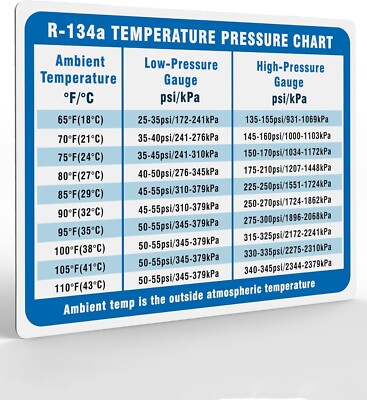
The R134a pressure temperature chart typically displays:
- Temperature: Usually in degrees Fahrenheit (°F) or Celsius (°C).
- Pressure: Typically in pounds per square inch gauge (psig) or kilopascals (kPa).
It’s important to remember that the chart shows the saturation point, where the refrigerant is in a state of equilibrium between liquid and vapor. Any deviation from the chart indicates that the refrigerant is either superheated (vapor) or subcooled (liquid).
*Note: This image is a general representation. Always refer to your specific equipment manufacturer’s chart for accurate data.*
How to Use the R134a Pressure Temperature Chart
Here’s a step-by-step guide to using the chart:
- Measure the pressure: Use a gauge manifold to measure the suction (low-side) and discharge (high-side) pressures of the system.
- Convert to temperature: Locate the measured pressure on the chart and find the corresponding saturation temperature.
- Compare with actual temperature: Measure the actual temperature of the refrigerant at the same point using a thermometer.
- Calculate superheat or subcooling:
- Superheat: Actual temperature – Saturation temperature (suction line).
- Subcooling: Saturation temperature – Actual temperature (liquid line).
- Analyze the results: Compare the calculated superheat and subcooling values with the manufacturer’s specifications to determine if the system is operating correctly.

Practical Applications
Let’s look at a few practical examples:
Example 1: Diagnosing a Leak
If the measured suction pressure is lower than expected for the given temperature, it could indicate a refrigerant leak. By using the chart, you can confirm the expected pressure and identify the discrepancy.
Example 2: Optimizing System Performance

Proper superheat and subcooling are essential for efficient system operation. Using the chart, you can verify that these values are within the recommended range and make adjustments as needed.
Key Considerations
- Accuracy: Ensure your gauges and thermometers are calibrated for accurate readings.
- Ambient conditions: Ambient temperature can affect system pressures, so consider this when analyzing the chart.
- System type: Different systems may have slightly different operating pressures and temperatures. Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Safety: Always follow safety procedures when working with refrigerants and HVAC equipment.
Conclusion
The R134a refrigerant pressure temperature chart is an indispensable tool for HVAC and refrigeration professionals. By understanding how to read and use it effectively, you can diagnose problems, optimize system performance, and ensure the longevity of your equipment. Remember to always prioritize safety and refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for accurate information. Mastering the use of this chart will elevate your technical skills and allow you to provide superior service.