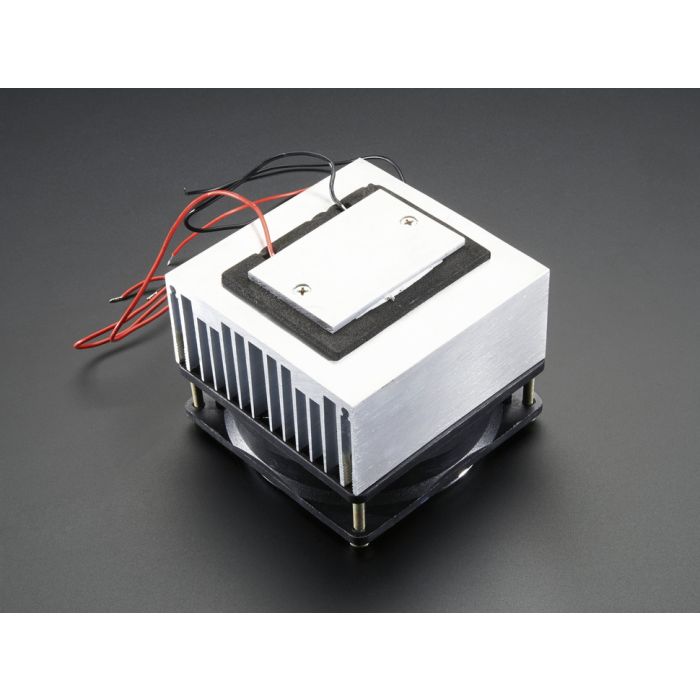

Welcome to the comprehensive guide on Peltier coolers, also known as thermoelectric coolers (TECs). These remarkable devices have revolutionized cooling technology in various applications, offering precise temperature control and compact designs. Let’s explore the science behind them and their diverse uses.
What is a Peltier Cooler?
A Peltier cooler is a solid-state device that transfers heat from one side to the other when an electrical current is applied. This phenomenon, known as the Peltier effect, allows these coolers to function without traditional refrigerants, making them environmentally friendly and versatile. Essentially, it’s a small heat pump that moves heat using electricity.
The Peltier Effect Explained
The core of a Peltier cooler is the Peltier effect, discovered by Jean Charles Athanase Peltier in 1834. When an electric current flows through two different conductors or semiconductors, a temperature difference occurs. One junction cools down, while the other heats up. This is because the current carries heat along with it. The efficiency of this process depends on the materials used and the magnitude of the current.
How Peltier Coolers Work
A typical Peltier cooler consists of an array of p-type and n-type semiconductor elements sandwiched between two ceramic plates. When a DC current is applied, electrons move from the p-type to the n-type material, carrying heat with them. This creates a temperature gradient, with one side becoming cold and the other hot. The hot side requires a heat sink to dissipate the transferred heat effectively. The efficiency of the cooler is directly related to how well the heat is removed from the hot side.
Advantages of Peltier Coolers
- Compact and Lightweight: Peltier coolers are small and light, making them ideal for applications where space is limited.
- No Moving Parts: They operate without mechanical moving parts, resulting in quiet operation and reduced maintenance.
- Precise Temperature Control: They offer accurate temperature regulation, allowing for precise control in critical applications.
- Environmentally Friendly: They don’t use refrigerants, making them eco-friendly.
- Versatile Applications: They can be used for both cooling and heating, depending on the direction of the current.
- Long Lifespan: Due to the lack of moving parts, they have a long operational life.
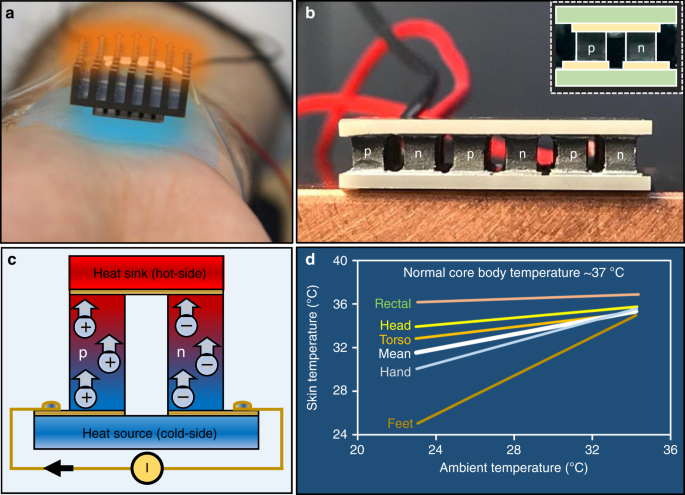
Limitations of Peltier Coolers
- Lower Efficiency: Compared to traditional vapor-compression refrigeration, Peltier coolers have lower efficiency.
- Heat Dissipation: The hot side requires efficient heat dissipation, which can be challenging in some applications.
- Limited Temperature Differential: They have a limited temperature difference they can achieve between the hot and cold sides.
- Power Consumption: They can consume significant power, especially when operating at high temperature differentials.
Applications of Peltier Coolers
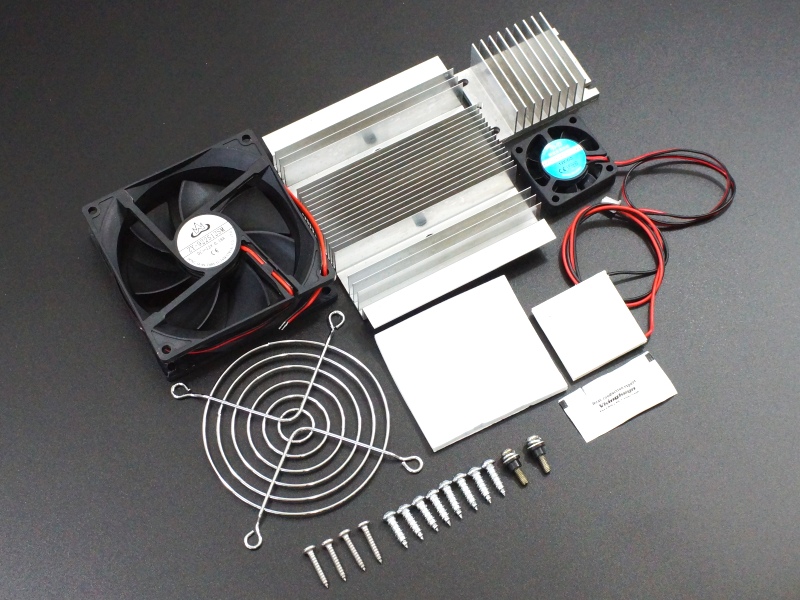
Peltier coolers are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Electronic Cooling: Cooling sensitive electronic components like CPUs and lasers.
- Medical Devices: Cooling samples, reagents, and medical equipment.
- Portable Coolers: Small refrigerators and coolers for personal use.
- Scientific Instruments: Maintaining precise temperatures in laboratory equipment.
- Automotive Applications: Cooling seats and other components.
- Telecommunications: Cooling optical devices and other equipment.
- Thermal Cycling: Used in PCR machines and other biological applications.
Specific Application Examples
Imagine a tiny portable fridge. A Peltier cooler is often at the heart of these devices. Because of their small size, they fit perfectly. In medical applications, they are used in devices that need to keep samples at a very precise temperature, where even a slight fluctuation could ruin a test. In high powered laser systems, the Peltier module is used to keep the laser diode at a stable temperature, which increases the lifespan and power output of the laser. In consumer electronics, they may be used in devices that need to stay cool, but can’t have a noisy fan. They are very useful in any environment where precise temperature control is necessary.
Choosing the Right Peltier Cooler
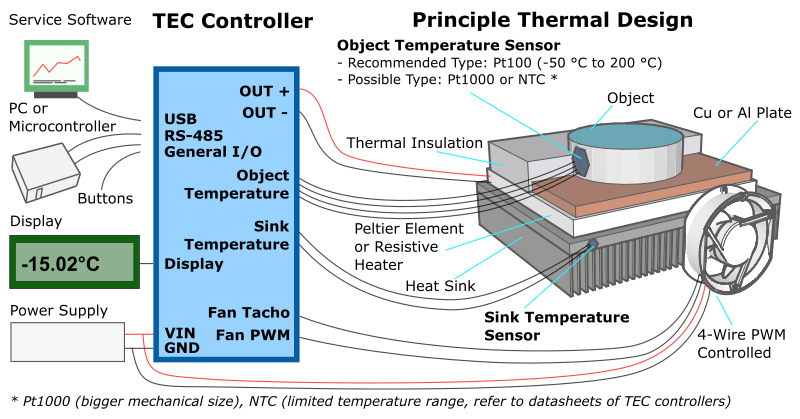
Selecting the appropriate Peltier cooler depends on several factors, including the required cooling capacity, temperature differential, and application environment. Consider the following:
- Cooling Capacity: Determine the amount of heat that needs to be removed.
- Temperature Differential: Calculate the difference between the hot and cold side temperatures.
- Power Requirements: Evaluate the power consumption and voltage requirements.
- Size and Mounting: Consider the physical dimensions and mounting options.
- Heat Sink: Choose an appropriate heat sink to ensure efficient heat dissipation.
Future of Peltier Cooling
Research and development in thermoelectric materials are ongoing, with the goal of improving efficiency and expanding applications. Nanotechnology and advanced materials are playing a crucial role in enhancing the performance of Peltier coolers. As technology advances, we can expect to see even more innovative uses for these versatile devices. The future of cooling may rely on advances in this technology.
In conclusion, Peltier coolers offer a unique and valuable solution for various cooling needs. Their compact size, precise temperature control, and environmentally friendly operation make them an excellent choice for numerous applications. Whether you’re cooling electronic components, medical samples, or personal beverages, Peltier coolers provide a reliable and efficient cooling solution.